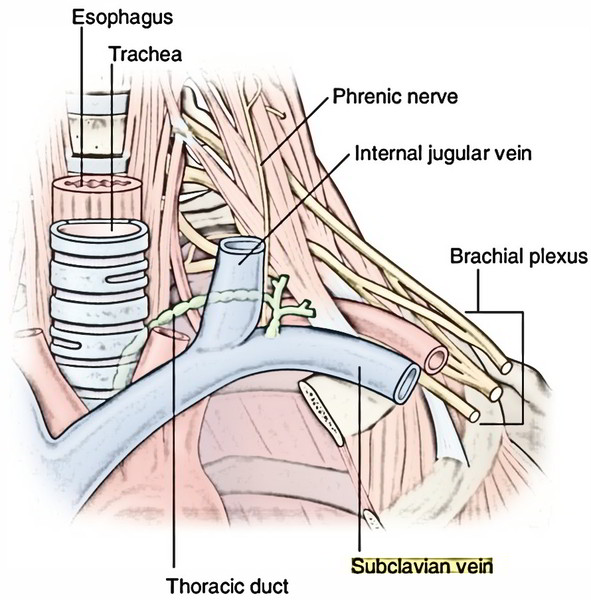
It stretches from the outer border of the very first rib to the medial border of the scalenus anterior, where it joins the internal jugular vein to create brachiocephalic vein and is the continuance of axillary vein. The subclavian vein is precisely the vein of the upper limb.
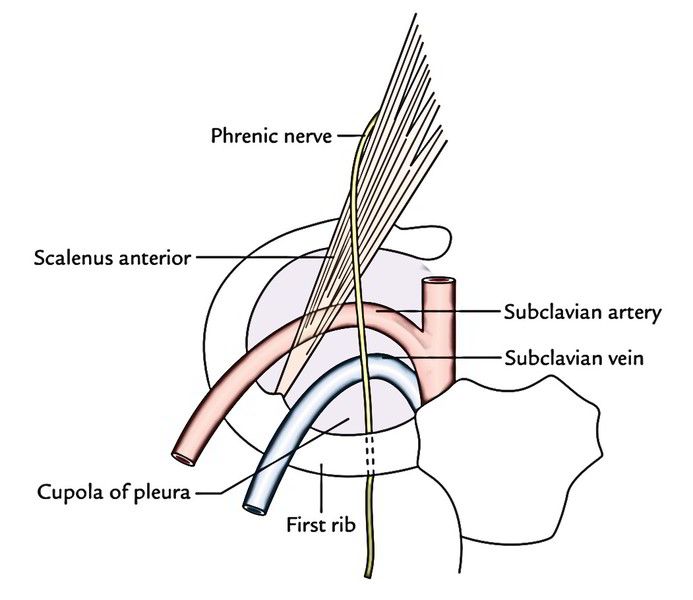
The subclavian vein at a level below the arch of the subclavian artery creates an arch on the other side of the pleura. They are divided from each other by the scalenus anterior in 2 arches.
It rarely rises above the level of the clavicle and possesses a pair of valves about 2 cm from its conclusion.
Connections
- In front: Clavicle and subclavius muscle.
- Behind: Subclavian artery with interceding scalenus anterior muscle and phrenic nerve.
- Below: First rib and cupola of pleura.
Tributaries
The tributaries of the subclavian vein are:
- External jugular vein.
- Dorsal scapular vein.
- Thoracic duct on the left side and right lymphatic duct on the right side.
- Anterior jugular vein.
- Cephalic vein.
Clinical Significance
Subclavian Vein Catheterization
The subclavian vein is situated immediately posterior to the medial third of the clavicle. From both below (infra-clavicular strategy) and above (supraclavicular method) the clavicle, It can be catheterized.
In infraclavicular method, the needle is inserted just below the lower border of the clavicle in the junction of its medial one-third and lateral two-third. The needle is pointed upwards and posteriorly in the direction of the middle of the jugular notch.
In supraclavicular method, the needle is inserted in the junction of lateral border of the clavicular head of sternocleidomastoid and upper border of the clavicle. The needle is pointed downwards and medially in the direction of the mediastinum.
Subclavian vein thrombosis: It can be impulsive (primary) or secondary. Medically, it presents as edema of the upper limb particularly after exercise. The primary thrombosis sometimes happens because of excessive and unaccustomed utilization of arm in the shoulder joint. The secondary thrombosis takes place as a complication of an indwelling venous catheter.

 (59 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)
(59 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)