The latticework of microfilaments and microtubules is stated to operate as a cytoskeleton. Cytoskeleton is the cellular organelle present throughout the cytoplasm. It identifies the shape of the cell and provides assistance to the cell. It is a complex network of structures with differing sizes. In addition to identifying the shape of the cell, it is likewise important for the cellular movements and the response of the cell to external stimuli.
The 3 classes of cytoskeletal are based upon their size and the types of protein they consist of. In order of size, beginning with the thinnest, they are
- actin filaments (microfilaments)
- intermediate filaments
- microtubules
Cytoskeletal Filaments
| Cell Parts | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Microtubules | Hollow cylinders composed of protein; 25 nm in diameter | Support the cytoplasm and form centrioles, spindle fibers, cilia, and flagella |
| Actin filaments | Small fibrils of the protein actin; 8 nm in diameter | Provide structural support to cells, support microvilli, are responsible for cell movements |
| Intermediate filaments | Protein fibers; 10 nm in diameter | Provide structural support to cells |
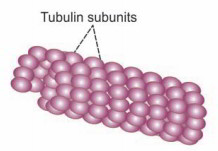
Microtubules
Microtubules are the straight, hollow and tubular structures of the cytoskeleton. These organelles without the restricting membrane are set up in various packages. Each tubule has a size of 20 to 30 nm. Length of microtubule differs and it might be 1000 times more than the thickness.
Structurally, the microtubules are formed by packages of globular protein called tubulin Tubulin has 2 subunits, specifically a-subunit and p-subunit.
Functions of Microtubules
Microtubules might operate alone or accompany other proteins to form more complex structures like cilia, flagella or centrioles and carry out numerous functions Microtubules:
- Identify the shape of the cell
- Provide structural strength to the cell
- Imitate conveyer belts which enable the movement of granules, vesicles, protein molecules and some organelles like mitochondria to various parts of the cell
- Form the spindle fibers which separate the chromosomes throughout mitosis
- Are accountable for the movement of centrioles and the complex cellular structures like cilia.
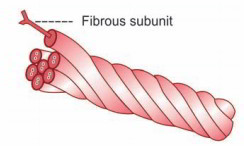
Intermediate Filaments
Intermediate filaments are the structures that form a network around the nucleus and encompass the periphery of the cell. Size of each filament has to do with 10 nm. The intermediate filaments are formed by rope-like polymers, which are composed of fibrous proteins
Subclasses of intermediate Filaments
Intermediate filaments are divided into 5 subclasses:
- Keratins (in epithelial cells)
- Glial filaments (in astrocytes)
- Neurofilaments (in nerve cells)
- Vimentin (in numerous types of cells)
- Desmin (in muscle fibers).
Functions of Intermediate Filaments
Intermediate filaments assist to keep the shape of the cell. These filaments likewise link the surrounding cells through desmosomes.
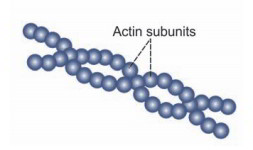
Microfilaments
Microfilaments are long and great thread-like structures with a size of about 3 to 6 nm. These filaments are composed of non-tubular contractile proteins called actin and myosin. Actin is more plentiful than myosin.
Microfilaments exist throughout the cytoplasm. The microfilaments present in ectoplasm consist of just actin molecules and those present in endoplasm consist of both actin and myosin molecules.
Functions of Microfilaments
Microfilaments:
- Provide structural strength to the cell
- Supply resistance to the cell versus the pulling forces
Are accountable for cellular movements like contraction, gliding and cytokinesis (partition of cytoplasm throughout cellular division).

 (58 votes, average: 4.48 out of 5)
(58 votes, average: 4.48 out of 5)