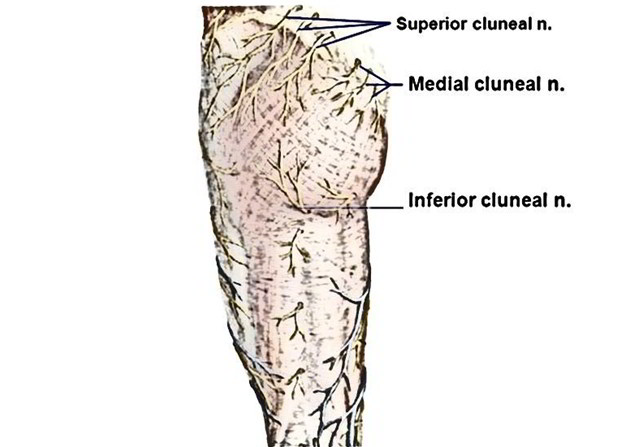
The Inferior Cluneal Nerve is also named as gluteal branch of posterior femoral cutaneous nerve. It arises as branch of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh. It innervate the skin of the lower part of the buttocks.
Origin
The inferior cluneal nerve, which emerges from the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, consists of sensory fibers emerging from the S2 root and is most often located in the midline of the sciatic nerve trunk.
Insertion
- The branches emerge along the lateral edge of the posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh they go around the edge in order to arrive at the dorsal side of the muscle, coming to the deeper plane of the dermal layers and sign up with the caudal edge of the gluteus maximus.
- The sensory perineal branch of the inferior cluneal nerve, which is generally particular, will cross back medially over the proximal insertions of the hamstring muscles.
- The number and pathways of the inferior cluneal nerve and its branches have many variants.
- Further onward, this perineal ramus splits into branches, a few of which will end at the lateral anal region, a couple of centimeters from the anus, and others that will terminate at the scrotum or at the labia majora.
- These divisions of the inferior cluneal nerve therefore overlap with the cutaneous area of the pudendal nerve.
Clinical Significance
- The inferior cluneal nerve or its branches can be credited to pain by sitting, which all, ultimately, originate from the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh.
- Lower butt pain is constant, so is pain situated in the fold under the butt and the posterior groin.
- The lateral anal area hurts however not the anal orifice itself, which in turn is an essential differential.
- Pain of the dorsal side of the thigh might be connected with inferior cluneal neuralgia.
- Any unilateral injury of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, in the circumstance of a piriformis syndrome.
- Therefore, be revealed by painful forecasts at the level of the thigh, in the posterior part of the gluteal region, however likewise in the perineal region especially while the person remains in a seated position.
- The pain should, nevertheless, not include the specific area of the pudendal nerve: the anus, clitoris, glans, and penis.

 (56 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)
(56 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)