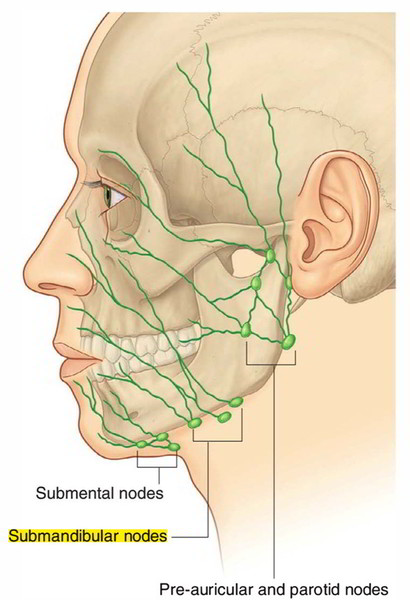
The submandibular lymph nodes sit between the submandibular salivary glands, which are underneath the tongue, and the mandible, or lower jawbone. Occasionally one or more of the lymph nodes may be embedded deep within the salivary gland.
The submandibular lymph nodes location is along the underside of the jaw on either side. It is responsible for lymphatic drainage of the tongue, submaxillary (salivary) gland, lips, mouth, and conjunctiva (mucous membrane that covers the eyeball and under surface of the eyelid). Infections of the following can cause the submandibular nodes to swell:
- Head
- Neck
- Sinuses
- Ears
- Eyes
- Scalp
- Pharynx
Swollen submandibular nodes usually indicate an active viral or bacterial infection and are commonly associated with infections of the sinuses, eyes, and ears.
Function
The submandibular nodes are small, usually measuring approximately 1 centimeter in a healthy adult. The submandibular duct, which brings lymph fluid to the node, is approximately 5 to 6 centimeters long in the average adult. The wall of the duct is thin and flexible. As the duct runs forward, it passes between the sublingual gland and genioglossus (the primary muscle of the tongue) to create an opening in the floor of the mouth. As the duct travels through the deepest part of the submandibular gland, it connects with tributaries draining into the lobe.

 (59 votes, average: 4.80 out of 5)
(59 votes, average: 4.80 out of 5)