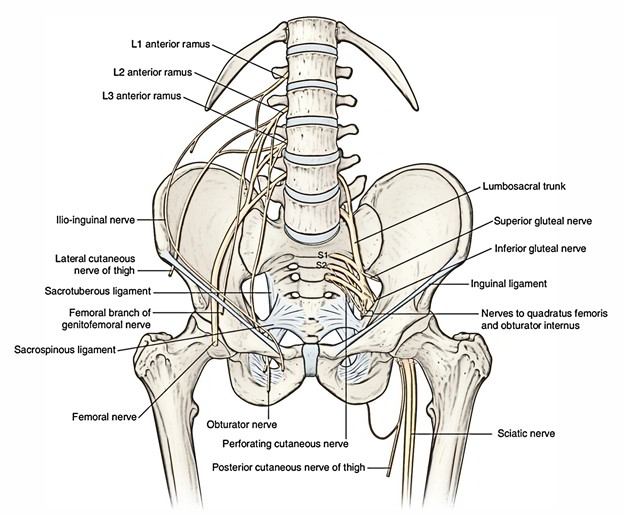
The inferior gluteal nerve is created from the posterior divisions of the L5, S1 and S2 nerve roots of the sacral plexus. The nerve is the primary motor nerve that provides the gluteus maximus muscle. Inferior gluteal is responsible for the motion of the gluteus maximus in activities requiring the hip to extend the thigh, such as climbing stairs.
Origin
- The interior gluteal nerve has its innervation via the SI and S2 roots however originates in a comparable style via the lumbosacral trunk.
- The nerve goes into the infra pirifomi foramen with the sciatic nerve, which is located laterally and routes interiorly.
- To innervate the gluteus maximus muscle and the hip capsule the inferior gluteal nerve exits the foramen and ramifies.
Insertion
The inferior gluteal nerve, created by divisions via the dorsal departments of L5 to S2, through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle, exits the pelvic cavity and supplies the gluteus maximus, the biggest muscle in the gluteal region. Each of superior and inferior gluteal nerves are accompanied by corresponding arteries.
Inferior to the piriformis muscle and throughout the posterior surface of the sciatic nerve, the inferior gluteal nerve goes into the gluteal region through the greater sciatic foramen.
Departments
The course of the nerve within the gluteus maximus muscle is short and it provides no cutaneous branches. The inferior third of the muscle and divides thoroughly to supply each ofthe the muscle and hip capsule the inferior gluteal nerve cleaves the deep surface of the gluteus maximums muscle along.
Function
- The significant function of the inferior gluteal nerve is to assist gluteus maximus to extend the bent thigh and lined up with the trunk.
- Via producing flexion at the supporting hip throughout bipedal gait, inferior gluteal nerve might avoid the forward momentum of the trunk.
- It is periodically involved in the walking cycle and in climbing up stairs and constantly involved in strong lateral rotation and abduction of the thigh
- Inferior gluteal nerve likewise assists gluteus maximus in supporting the femur on the tibia when the knee extensors are unwinded. In addition to this, the inferior gluteal nerve holds a crucial function throughout some functions like running or standing
- Gluteus maximus is a large muscle with many functions, and is powerful extensor of the thigh or the trunk lower limbs remain in a fixed position.
Clinical Significance
- Inferior gluteal nerve injury leads to weak point and atrophy of the gluteus maximus with impaired leg extension.
- A deep hurting pain might be informed, especially in association with tumors compushing the nerve.
- Unless there is participation of surrounding sensory nerves, such as the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve no true sensory disability happens.
- Since gluteal neuropathies usually happen after surgery or trauma, distinguishing a neurological deficit by health examination might be difficult.
- Weak point of abduction after hip surgery can be very challenging to distinguish via neuropathic weak point and can likewise cause by injury or rupture to the abductor muscle tendons.
- As separated gluteal nerve compression is unusual, consisting of observation and physical treatment, which might consist of electrotherapy of the muscles its treatment must be based upon a conservative technique.
- Secret to protecting one’s variety of activity should the nerves recuperate is Physical treatment.
- The most effective treatment is to secure the patient who is catatonic or under anesthesia from having direct pressure in this region.
- Earlier surgical treatment might be needed to repair direct permeating trauma, iatrogenic injury, or serious pelvic misalignment.

 (56 votes, average: 4.81 out of 5)
(56 votes, average: 4.81 out of 5)