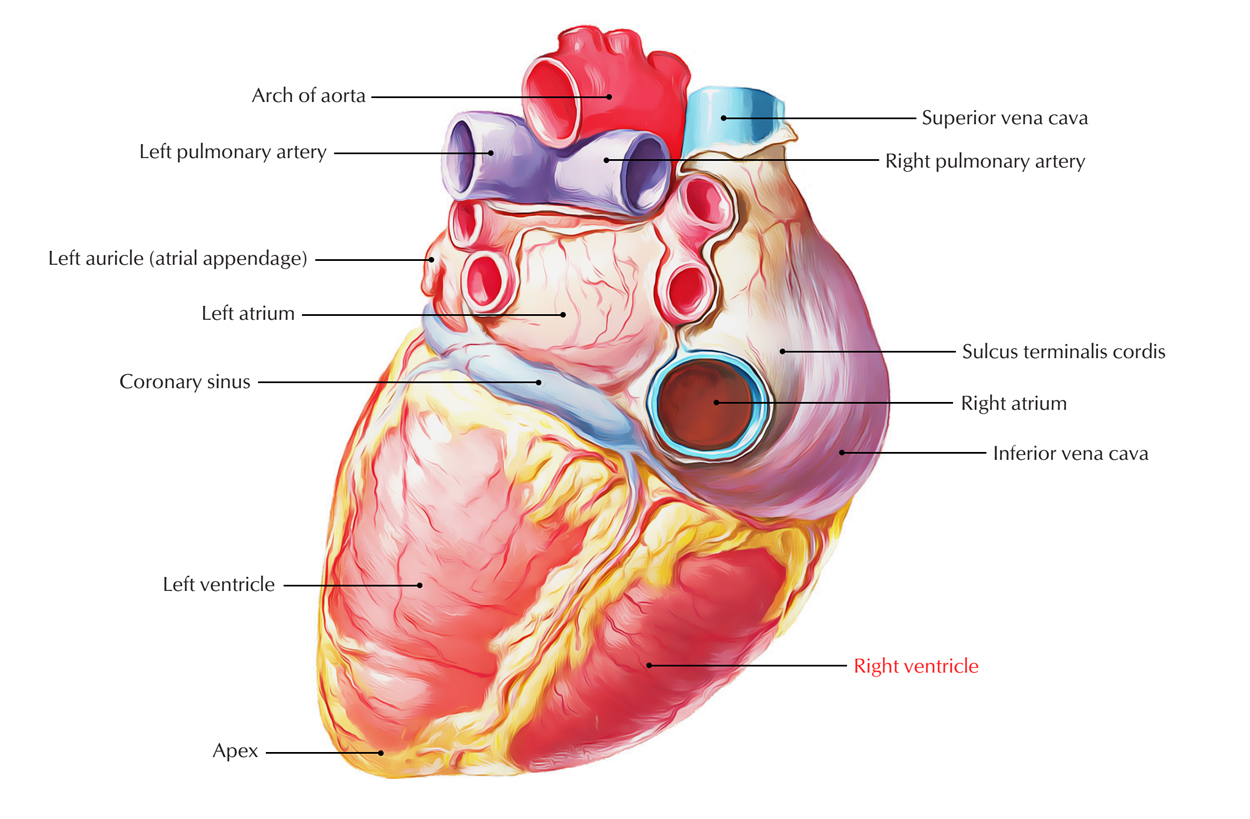
The right ventricle is the triangular compartment of the heart that interacts with the right atrium via right atrioventricular orifice as well as via pulmonary orifice with the pulmonary trunk.
Right Ventricle
Position
- In the anatomical position, the right atrium is towards the right of the right ventricle and the right ventricle is located in front of and towards the left of the right atrioventricular orifice.
- So, the blood going inside the right ventricle from the right atrium travels in a horizontal and forward direction.
- The right ventricle creates most of the anterior surface of the heart as well as a part of the diaphragmatic surface.
External Features
- It creates the most of sternocostal surface along with the small part of the diaphragmatic surface of the heart. The inferior border is also created by it.
- A relatively vertical anterior portion of the coronary sulcus or atrioventricular groove separates it from the right atrium.
Internal Features
- The interior of right ventricle consists of two parts:
- A large, lower rough inflowing part.
- A small upper outflowing part, the infundibulum.
- The two parts are separated from each other by a muscular ridge, the supraventricular crest a.k.a. infundibuloventricular crest.
- The forward prominence of the interventricular septum flattens the cavity of right ventricle. It has crescent form in transverse section.
- The wall of the right ventricle is thinner compared to the left ventricle (ratio 1:3).
Trabeculae Carneae
A sponge-like appearance is given to the ventricular chamber by these muscular projections. Trabeculae carneae or papillary muscles have one end connected towards the ventricular surface, and the other end connects to the chordae tendinae, that connects to the free edges of the cusps of the tricuspid valve. In the right ventricle, there are three papillary muscles:
- Ariseing from the anterior wall of the ventricle, the anterior papillary muscle is the largest and most constant papillary muscle.
- With some chordae tendineae arising directly from the ventricular wall, the posterior papillary muscle may consist of one, two, or three structures.
- With chordae tendineae emerging directly from the septal wall the septal papillary muscle is the most inconsistent papillary muscle, being either small or absent.
Moderator band (Septomarginal Trabeculum)
Across the ventricular cavity, moderator band is a thick muscular ridge spreading out from ventricular septum towards the base of the anterior papillary muscle. It transports the right branch of the atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His) that is a part of conducting system of the heart. Overdistension of right ventricle is prevented by it.
Conus Arteriosus (Infundibulum)
The outflow tract of the right ventricle is the conus arteriosus a.k.a. infundibulum that leads to the pulmonary trunk. This area originates from the embryonic bulbus cordis and possesses smooth walls.

 (58 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)
(58 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)