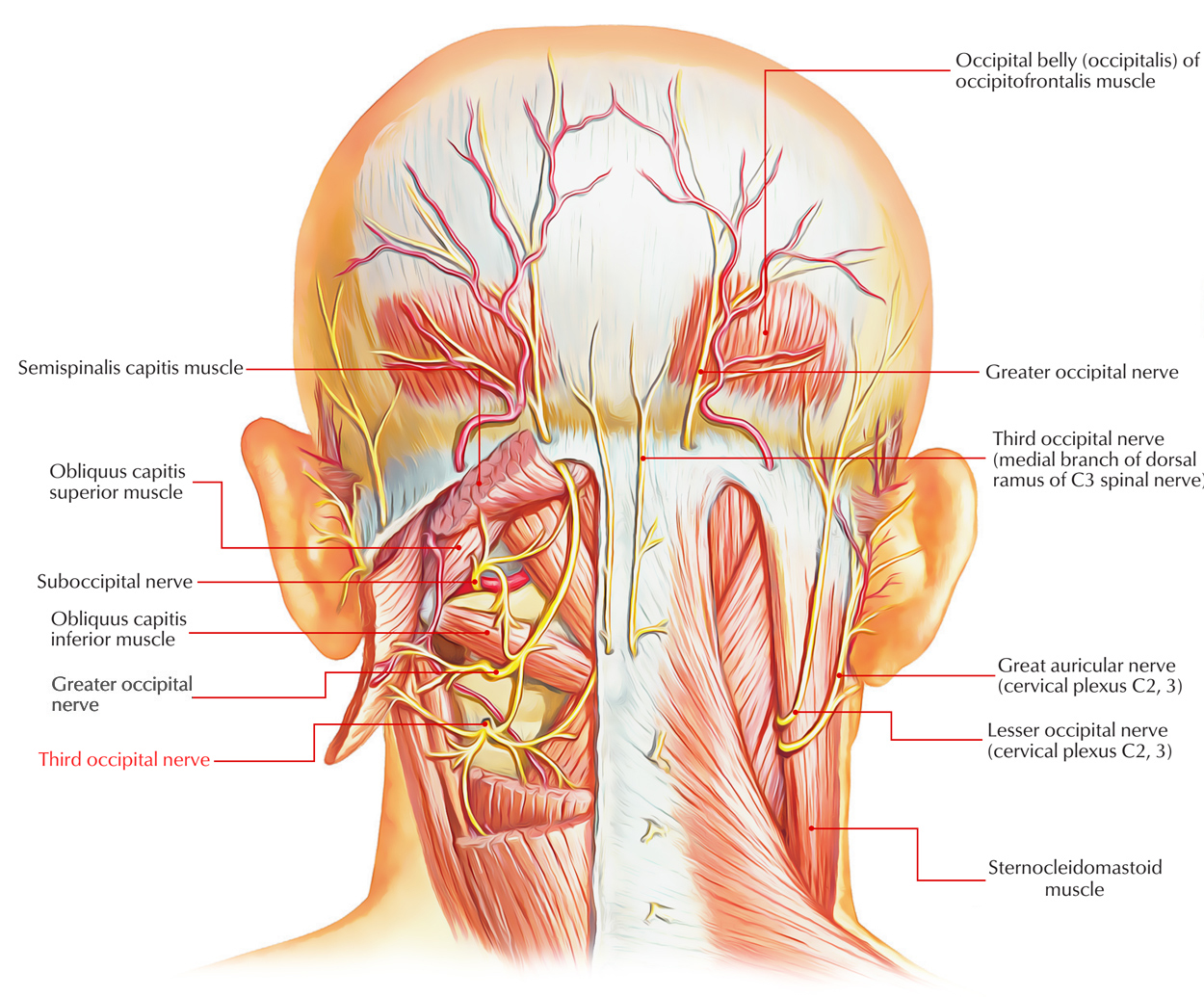
The C3 spinal nerve splits into an anterior ramus along with a posterior ramus.
- The posterior ramus divides into two medial branches and a lateral branch.
- The larger, superior medial branch is the third occipital nerve.
- From superior branch fibers of the third cervical nerve the third occipital nerve emerges at the level of the trapezius muscle.
Third Occipital Nerve
Insertion
Around the superior articular process of the C3 vertebra, the third occipital nerve travels backwards and medially. Either just under or across the joint margin it travels through the C2-C3 facet joint. Primarily, the nerve supply of the C2-C3 facet joint is from the large, superior medial branch of the C3 spinal nerve and the third occipital nerve.
- Near the superior articular process of the C3 vertebra, the third occipital nerve travels dorsomedially.
- Fibers from the third occipital nerve supply the primary innervation of the C2 to C3 facet joints with some contribution from the C3 medial branch and small interacting fibers from the second cervical nerve.
- Afterwards fibers of the third occipital nerve travel superiorly in order to give sensory innervation to the ipsilateral suboccipital region.
Structure
The third occipital nerve is thicker compared to other medial branches. Over the occipital region behind the ear, it carries a few sensory fibers from a small piece of skin. Other medial branches generally do not carry skin sensation and this makes a difference to the observations after a TONB.
The general route of the third occipital nerve is forward over the C2-3 in the pericapsular fascia in order to join its dorsal ramus within the C2-3 intervertebral foramen. The course varies among individuals so the nerve travels somewhat horizontally transversely the joint at a plane that extends among the top and just underneath the bottom of the intervertebral foramen.
Function
It supplies:
- The C2–C3 zygapophysial joint while laterally passing from the joint.
- Also it supplies part of the semispinalis capitis muscle.
- Its cutaneous branch supplies suboccipital region.
Clinical Significance
Third Occipital Nerve Block
The test procedure at the C2-3 level that is compatible to lower cervical levels is referred to as a third occipital nerve block.
To ensure blockade of the third occipital nerve happens to be in this range requires injections of 0.3 ml of local anesthetic at each of three target points, which are located within a vertical line over the middle of the joint:
- High one at the level of the apex of the C3 superior articular process.
- Low one at the level of the bottom of the C2-3 intervertebral foramen.
- Middle one halfway between the other two.

 (48 votes, average: 4.51 out of 5)
(48 votes, average: 4.51 out of 5)