Tibialis anterior is a multipennate and spindle-shaped muscle. It lies against the lateral surface of the tibia and is the most medial and superficial dorsiflexor of the foot.
Tendon of tibialis anterior: At the time when foot is inverted it becomes prominent. Across the medial part of the anterior aspect of the ankle, it is seen passing downward and medially.
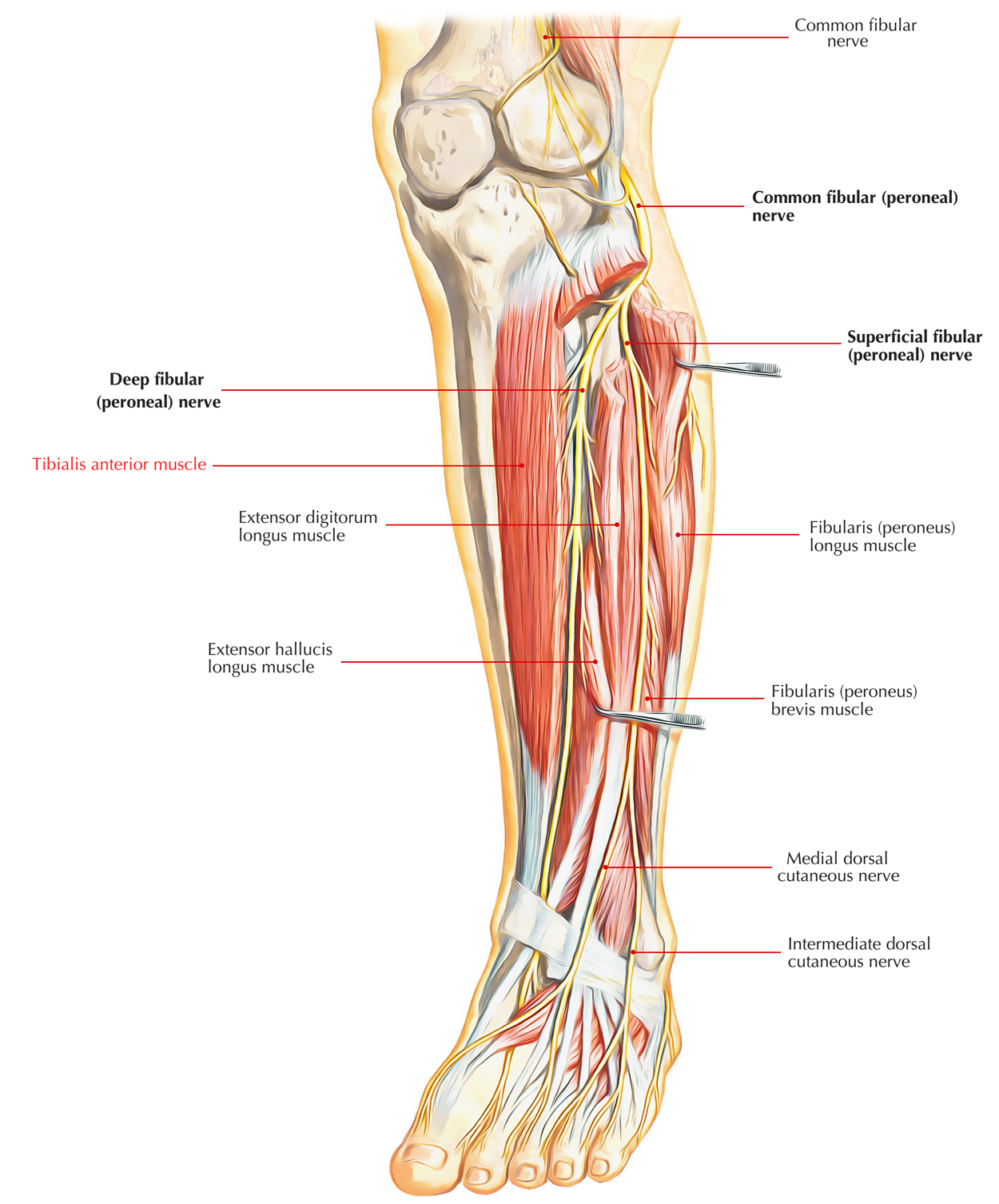
Tibialis Anterior Muscle
Origin
It emerges from:
- Upper two-third of the lateral surface of the tibia and adjacent part of the lateral condyle of the tibia.
- Adjoining part of the interosseous membrane.
- Overlying deep fascia of the leg.
Insertion
It passes through the medial part of superior extensor retinaculum and the upper band of inferior extensor retinaculum. The muscle fibres assemble below to form a tendon which is related to the lower one-third of the lateral surface of the tibia. Now to be inserted on to the inferotendial side of the base of the first metatarsal bone and surrounding part of the medial cuneiform, it medially passes underneath the inferior band of inferior extensor retinaculum.
Nerve supply
The deep peroneal nerve innervates tibialis anterior.
Functions
- The tibialis anterior assists in any activity which needs moving the leg or keeping the leg vertical like walking, running, treking, kicking a ball, and so on
- It functions to support the ankle as the foot strikes the ground throughout the contact phase of walking (eccentric contraction) and later to pull the foot clear of the ground during the swing stage (concentric contraction).
- It likewise operates to ‘lock’ the ankle, when kept in an isometric contraction as in toe-kicking a ball
- Dorsiflexion and Nerve supply of the foot is overseen by tibialis anterior.
Actions
- At the ankle joint, it is the chief dorsiflexor of the foot.
- It maintains the medial longitudinal arch.
- At the midtarsal and subtalar joints, it functions as an inverter of the foot.
Clinical Significance
If usual, its tendon can be seen and palpated. To test tibialis anterior clinically, the patient is asked to stand on heels or dorsiflex the foot against resistance.
Clinical Connection
Anterior tibial compartment syndrome/shin splints (Fresher’s Syndrome):
- It happens particularly when the untrained persons who lead an inactive life are asked to stroll or run for long distances due to overexertion of the muscles of the anterior compartment. Shin splints likewise occur in trained runners who do not warm-up.
- Due to sudden overuse which may impede venous return leading to accumulation of more fluid inside the compartment with unyielding walls muscles of the compartment swell within a tight compartment.
- The pressure has the tendency to compress the anterior tibial artery, and decreasing the blood supply to the muscles, causing ischemia and pain.
- It is frequently seen in freshers (e.g. newly admitted medical students/newly recruited army personnel) who are made to run exceedingly. Hence, this condition is also described as army fresher’s syndrome.

 (54 votes, average: 4.72 out of 5)
(54 votes, average: 4.72 out of 5)