Zygapophyseal Joints are joints that are located in the middle of the superior and inferior articular processes of adjacent vertebrae. Structural resistance to anterior shear forces in the lumbar segments is given by the shape of the zygapophyseal joints, the zygapophyseal joint capsules, the fibers of the anulus fibrosus and the iliolumbar ligaments in the lower segments.
Zygapophyseal Joints (Facet Joints)
Individual alteration in structure of the joint can be an agonistic feature to pain within this region. The capsuloligamentous structures will be strained, if an individual has zygapophyseal joints sloping totally in the sagittal plane and ultimately they may get elongated and cause pain, due to the reason that they are innervated structures.
Regions
The zygapophyseal joints facilitate the flexion and extension of the vertebral column and they also inhibit the vertebrae from sliding forward in cervical, thoracic and lumbar zones:
- In cervical zone, the zygapophyseal joints angle inferiorly from anterior to posterior. This enables in looking sideways and upwards. In cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions, the direction of these joints varies.
- In the thoracic zone, the zygapophyseal joints are positioned vertically. This limits flexion and extension but facilitates rotation.
- In the lumbar zone, the zygapophyseal joints have rounded joint surfaces and adjacent articular processes interlock with each other. This phenomenon confines the range of movements in this region; however the remaining major movements in the lumbar region are flexion and extension still.
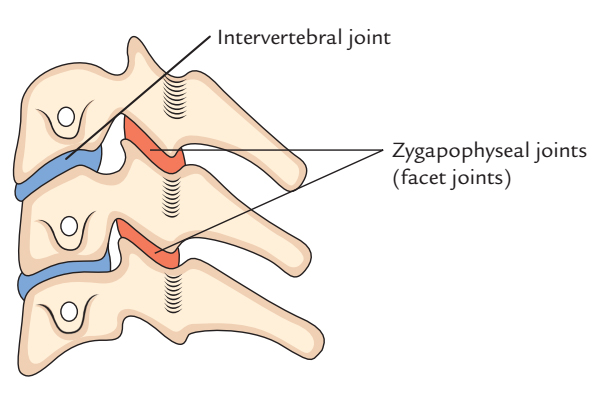
Zygapophyseal Joints (Facet Joints)
Type
These are plane category of synovial joints. Hyaline cartilage covers the articular surfaces. The articular surfaces are inclined horizontally and from anterior to posterior slope inferiorly. This enables the rotation of neck in looking sideways and upwards.
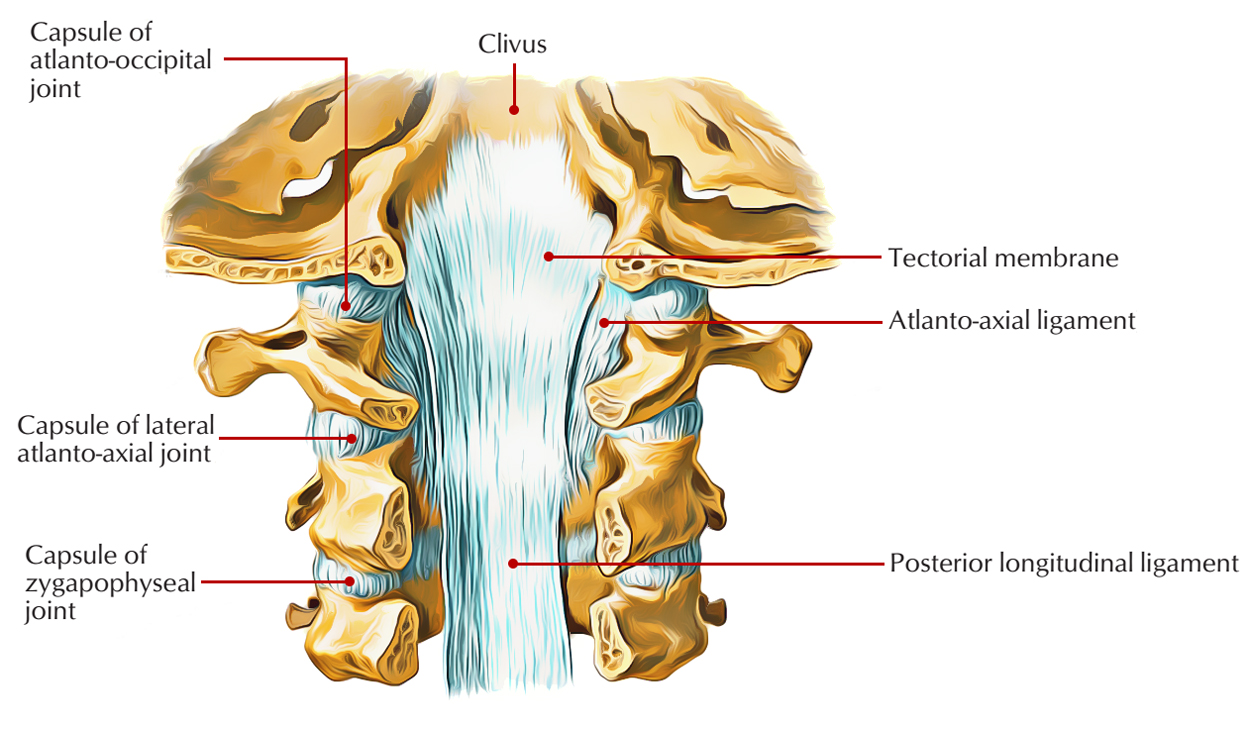
Ligaments
Fibrous capsule is structurally thin and loose and it is attached to the periphery of articular facets.
Movements
Side-to-side rotation of the neck is facilitated by it.
Clinical Significance
Dislocation
It only happens in cervical zone due to the inclination of the articular surfaces of articular processes. Dislocations are always associated with fracture of articular processes in thoracic and lumbar regions. Mostly, the dislocations occur in the middle of 4th and 5th or among 5th and 6th cervical vertebrae.
Facet Joint Syndrome
Facet syndrome along with degenerative disc disease is assumed to be one of the most common reasons of lower back pain, a discrete but functionality associated disorder. Facet syndrome is a condition where the facet joints that is synovial diarthroses, from C2 to S1 deteriorate and create painful symptoms. It is also known as facet joint disease, facet osteoarthritis, and facet hypertrophy or facet arthritis.
Osteoarthritis
The hands, feet, spine, and the large weight-bearing joints, such as the hips and knees are commonly affected in osteoarthritis although hypothetically, any joint in the body can be affected by it. Typically as osteoarthritis grows, movement patterns such as gait are affected. The most common cause of a joint effusion of the knee is osteoarthritis.

 (49 votes, average: 4.69 out of 5)
(49 votes, average: 4.69 out of 5)