The costodiaphragmatic recesses are the largest and clinically vital recesses. It is an entrenched channel which is located at the lower border of the chest wall in the middle of the costal pleura and the diaphragmatic pleura. They are deepest after forced expiration and shallowest after forced inspiration.
Costodiaphragmatic Recess
Structure
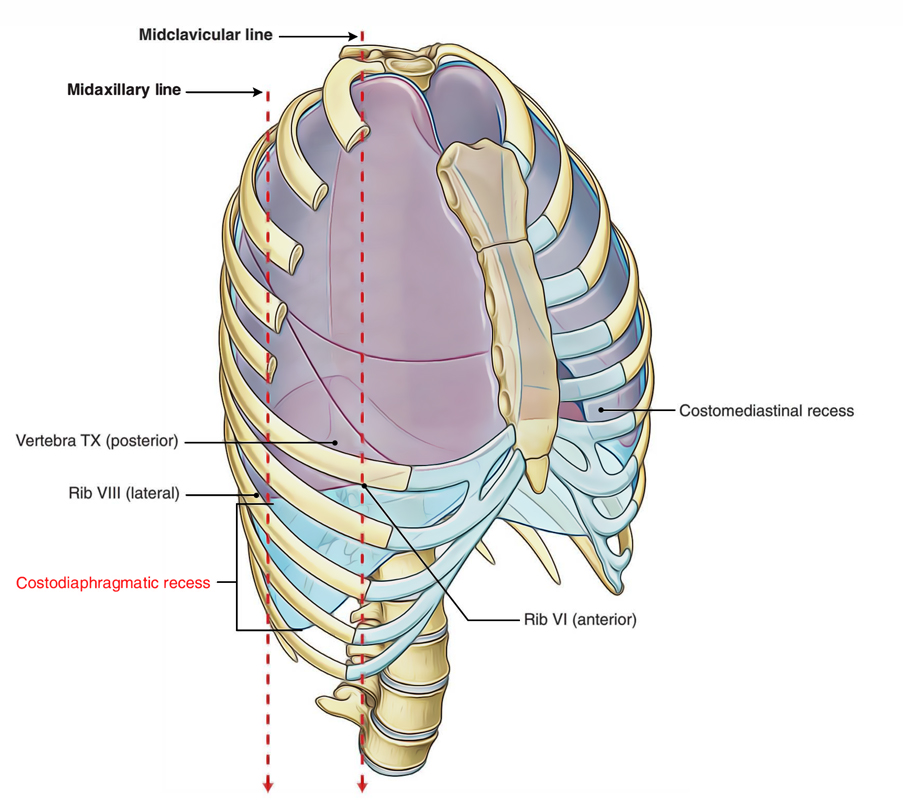
The costodiaphragmatic recess is also known as the costophrenic recess or phrenicocostal sinus is a possible room in the pleural cavity at the posterior-most tips of the cavity located in the costophrenic angle at the connection of the costal pleura and diaphragmatic pleura. It is vertically 5 cm in length and alongside the mid-axillary line it spans from the eighth to the tenth rib.
During quiet respiration:
- Within the midclavicular line, the inferior margin of the lung crosses rib VI and rib VIII in the midaxillary line.
- In order to arrive at the vertebral column, goes a bit straight at vertebral level TX.
The inferior margin of the lung can be evaluated via a line running in the middle of ribs VI, Rib VIII and vertebra TX through the midclavicular line and near the thoracic wall towards the vertebral column.
Similarly the inferior margin of the pleural cavity is rib VIII, rib X, and vertebra TXII.
Functions
This reserve space open out at the time of deep inspiration and the lungs move in deep up to two intercostal spaces into the recess.
Clinical Significance
Pleural Effusion
A pleural effusion is excess fluid that gathers within the pleural cavity, the fluid-filled space which encloses the lungs. This excess can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs.
In the costodiaphragmatic recess, the costodiaphragmatic angle is disturbed creating widening of the angle whenever a small volume of fluid accumulates.
In X-ray of chest, it appears as radiopaque darkness as a fluid line. It can be the first symptom of pleural effusion. Consequently pleural recesses are examined regularly in the thoracic X-Rays.

 (54 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)
(54 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)