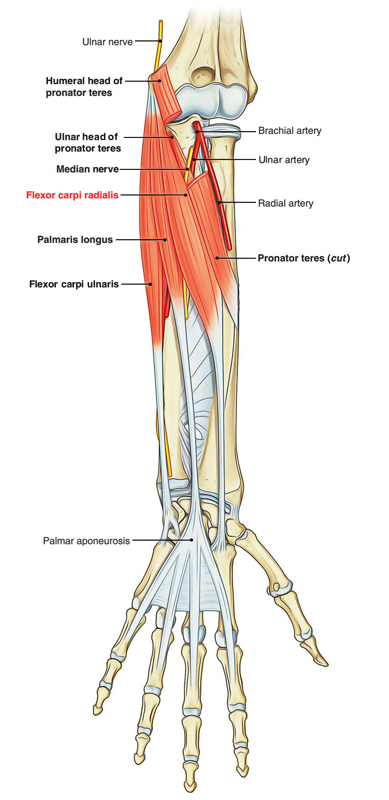
It originates via a common flexor origin from the medial epicondyle of humerus. The entire flexor carpi radialis lies oblique on the forearm, as it travels via its emergence towards its insertion in the anatomical situation that is supinated forearm.
Flexor Carpi Radialis
Insertion
It inserts on to the anterior sides of the bases of second and third metacarpals
Structure
Located on the upper half of the forearm, the flexor carpi radialis is a little flattened distally with a fleshy belly. Starting one-third of the way down the forearm its tendon is flat, wide, and directed proximally and also circular distally. The muscle fibers of the belly split and for a short distance travel downwards to each aspect of the tendon. Due to this type of arrangement, the wide proximal end of the tendon generally gets slightly lowered within the bulging V-shaped distal ends of the belly whenever the muscle is strained. The muscle fibers on the radial portion of the tendon afterwards blend visually with the shape of the brachioradialis. Just proximal towards the wrist, specifically whenever the wrist is flexed as well as radially deviated the cordlike tendon of the flexor carpi radialis is very prominent. It is located just over the midline, towards the radial aspect of the forearm. This tendon is thicker than the tendon of the palmaris longus, whenever the hand is straight is pointed toward the index finger, and also goes out of vision at the base of the hand.
Nerve Supply
Arterial Supply
Actions
- It flexes the wrist together with flexor carpi ulnaris
- together with brachioradialis, it abducts the wrist
Attachments
- The flexor carpi radialis muscle has a large and protuberant tendon in the distal half of the forearm and also is lateral towards the palmaris longus.
- The tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle is situated just lateral towards the midline, unlike the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris, which creates the medial margin of the distal forearm.
- In this position, the tendon could be easily palpated, making it an essential landmark for finding the pulse in the radial artery, which lies directly lateral to it.
- The tendon of the flexor carpi radialis travels via a chamber created by bone as well as fascia at the lateral aspect of the anterior surface of the wrist and also attaches to the anterior sides of the bases of metacarpals II and III.
- The flexor carpi radialis is a highly effective flexor of the wrist and can also abduct the wrist.

 (57 votes, average: 4.79 out of 5)
(57 votes, average: 4.79 out of 5)