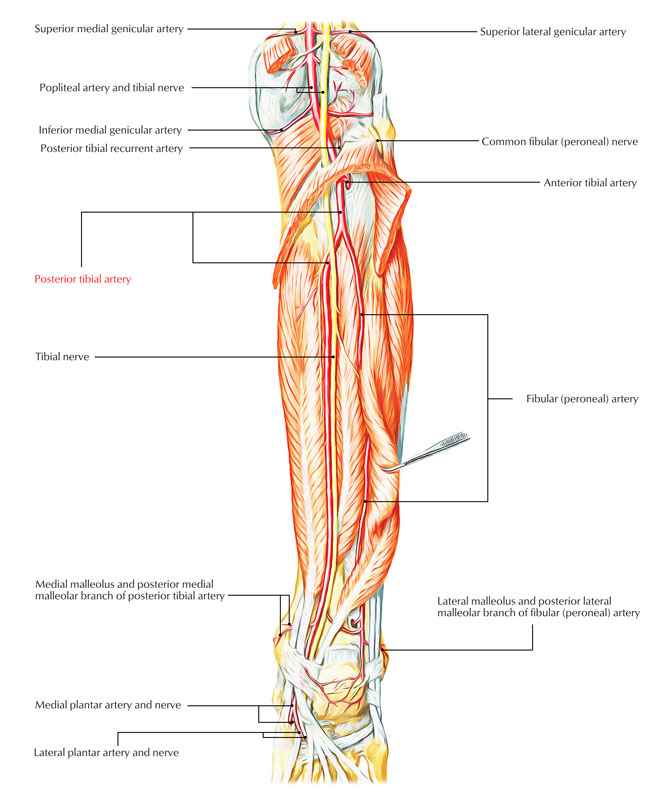
Origin
Posterior Tibial Artery is the bigger branch of both terminal branches of the popliteal artery because its branches not only supply the posterior compartment but also the lateral compartment of the leg and the sole of the foot.
Course and Relationships
- It starts at the lower border of popliteus, between the tibia and fibula, deep to gastrocnemius and enters the rear of the leg by passing deep to the tendinous arch of soleus.
- In the leg, it goes downward and somewhat medially to reach the posteromedial side of the ankle, midway between the medial malleolus and the medial tubercle of calcaneum.
- It ends deep to the flexor retinaculum by splitting into a large lateral plantar artery and a small medial.
- Throughout its course, it’s escorted by the tibial nerve, which crosses the artery from the medial to lateral side.
Branches
- Peroneal (fibular) artery: It’s the biggest and most important branch of the posterior tibial artery. The point of origin is 2.5 cm distal to the inferior border of popliteus.
- Muscular branches: To the muscles of posterior compartment.
- Nutrient artery to tibia: It’s the largest nutrient artery within the body. It goes into the nutrient foramen of tibia below the soleal line.
- Circumflex fibular artery: It encircles the lateral side of the neck of the fibula.
- Communication branch: It joins together with the quite similar branch of peroneal artery about 5 cm above the ankle.
- Medial malleolar branch: It enters toward the medial malleolus.
- Calcaneal branch: It pierces the flexor retinaculum and supplies soft tissues of the heel.
- Terminal branches: All these are medial and lateral plantar arteries of the sole.
Clinical significance
Posterior tibial pulse: It can be felt against the calcaneum about 2 cm below and behind the medial malleolus, and in front of the medial border of the tendocalcaneus. Since the posterior tibial artery is located deep to the flexor retinaculum, it’s significant to request the patient to invert his or her foot to relax the flexor retinaculum. Failure to do so may result in an erroneous judgment that this pulse is absent.

 (60 votes, average: 4.78 out of 5)
(60 votes, average: 4.78 out of 5)