The mandible is the only mobile bone of the face. The mandible is horizontal and has a horseshoe-shaped body along with two vertical expansions referred to as rami. (Singular – Ramus)
Structure
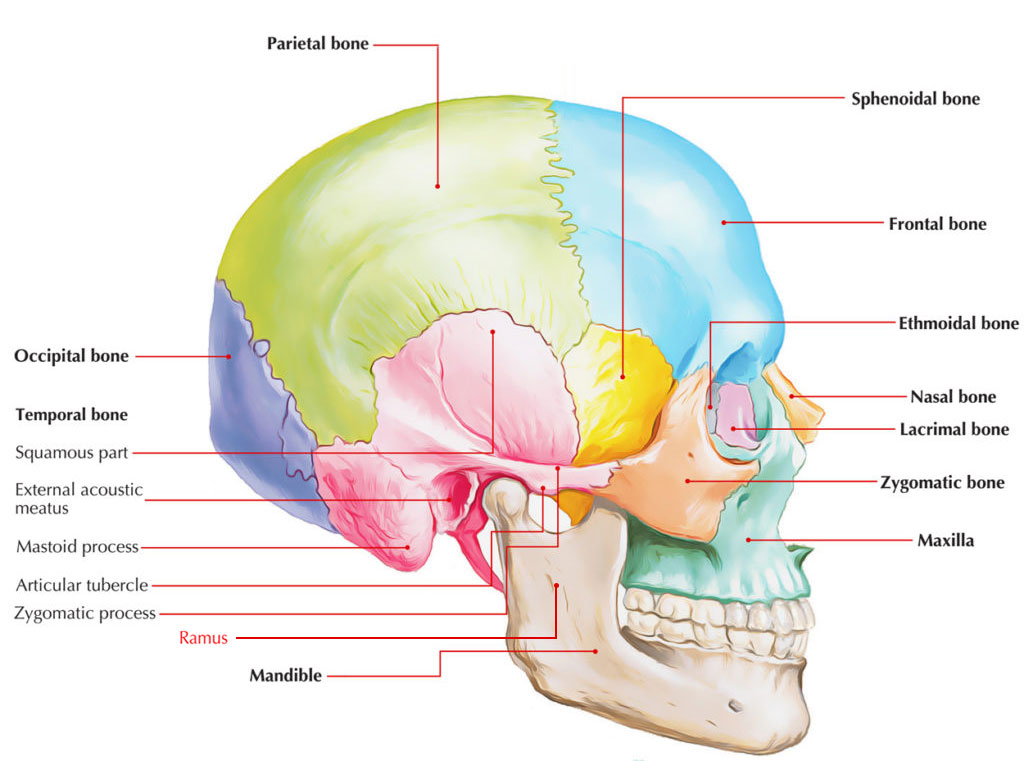
Ramus of Mandible
The body of each ramus goes downward from the top of the rami.
- The mandibular foramen is found on the inside of the body of the ramus, which is the beginning of the internal oblique ridge.
- The internal oblique ridge a.k.a. the mylohyoid ridge along with the body of the mandible travels along with the inner side of the ramus.
- The angle of the mandible is the point where the ramus merges with the body of the mandible on the outside margin.
Features
The ramus presents the following features:
1. Two surfaces
a) Lateral surface.
b) Medial surface.
2. Four borders
a) Anterior
b) Superior is serrated in order to create mandibular notch.
c) Inferior
d) Posterior
3. Two processes
a) Condylar process is a strong upward protrusion from posterosuperior portion.
b) Coronoid process is a compressed triangular projection from anterosuperior portion from one side to another side.
4. The mandibular canal
Mandibular canal travels obliquely downward and forward inside the ramus and afterwards horizontally forward in the body, where it is found under the alveoli and interacts with them via small openings. On arriving at the incisor teeth, it turns backwards in order to connect with the mental foramen, produces two small canals which travel towards the cavities possessing the incisor teeth. It contains the inferior alveolar vessels as well as nerve through which branches are circulated towards the teeth via the incisive nerve.

 (60 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)
(60 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)