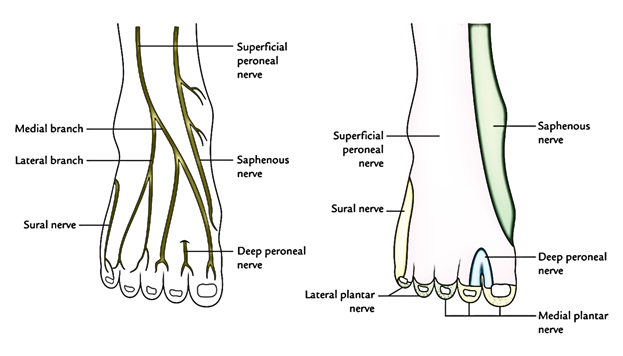
Sensory Innervation of The Dorsum of The Foot
4 sets of nerves supply the sensory nervous supply to the dorsum of the foot :
- Superficial peroneal (musculocutaneous) nerve: With the exception of the skin of the cleft between the first and 2nd toes. it supplies sensory nerves to the majority of the dorsum of the foot . It also supplies medial margin of the great toe.
- Deep peroneal nerve: It gives nerve supply to the cleft between the first and 2nd toes.
- Sural nerve: It supplies lateral margin of the dorsum of the foot and lateral margin of the little toe.
- Saphenous nerve: It supplies medial margins of the dorsum of the foot up to the head of the very first metatarsal.
Muscles of The Dorsum of The Foot
All these are as follows:
- Extrinsic tendons of the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg (viz., tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, and peroneus tertius).
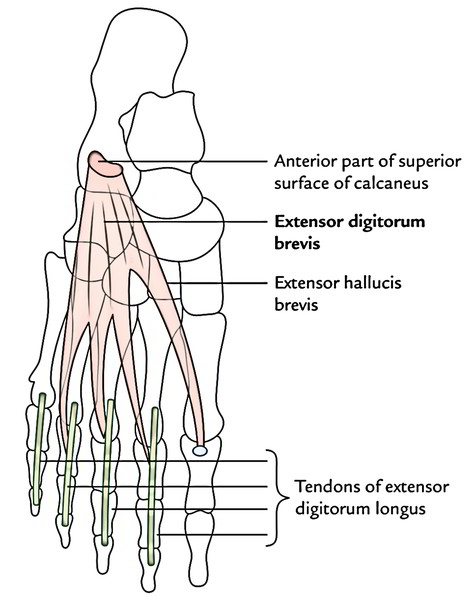
- Intrinsic muscle on the dorsum of the foot is only one – the extensor digitorum brevis.
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
It’s a small muscle situated on the lateral part of the dorsum of the foot, deep to the tendons of extensor digitorum longus. It’s the only muscle on the dorsum of the foot and creates a fleshy swelling anterior to the lateral malleolus. The young beginner physicians sometime diagnose it as a contusion.
Origin
It originates from the anterior part of the superior surface of calcaneum, medial to the connection of the stalk of inferior extensor retinaculum.
Insertion
- The muscle splits into 4 tendons for the medial 4 toes. The tendon to the big toe crosses in front of dorsalis pedis artery and inserts on the dorsal surface of the proximal phalanx of the big toe. The Lateral 3 tendons join the lateral side of the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus to the 2nd, third, and fourth toes.
- Medial most part of the extensor digitorum brevis, which creates the tendon for the big toe, splits or becomes different early. It’s called extensor hallucis brevis.
Nerve Supply
It’s by the lateral terminal branch of the deep peroneal nerve.
Actions
- Extensor hallucis brevis (EHB) stretches the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
- The other 3 tendons stretch the metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of 2nd, third, and fourth toes, especially when the foot is dorsiflexed.
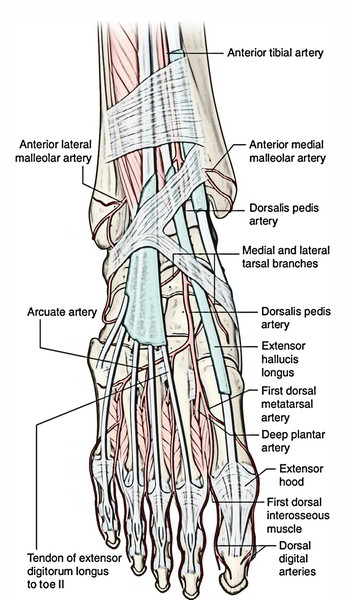
Dorsalis Pedis Artery
The dorsalis pedis artery is the just the continuation of the anterior tibial artery. So it starts as the anterior tibial artery passes by the ankle joint. It goes anteriorly over the dorsal aspect of the talus, navicular, and intermediate cuneiform bones, and then passes inferiorly, as the deep plantar artery, between the two heads of the first dorsal interosseous muscle to join the deep plantar arch in the sole of the foot. The pulse of the dorsalis pedis artery on the dorsal surface of the foot can be felt by gently palpating the vessel against the underlying tarsal bones between the tendons of the extensor hallucis longus and the extensor digitorum longus to the second toe.

 (45 votes, average: 4.54 out of 5)
(45 votes, average: 4.54 out of 5)