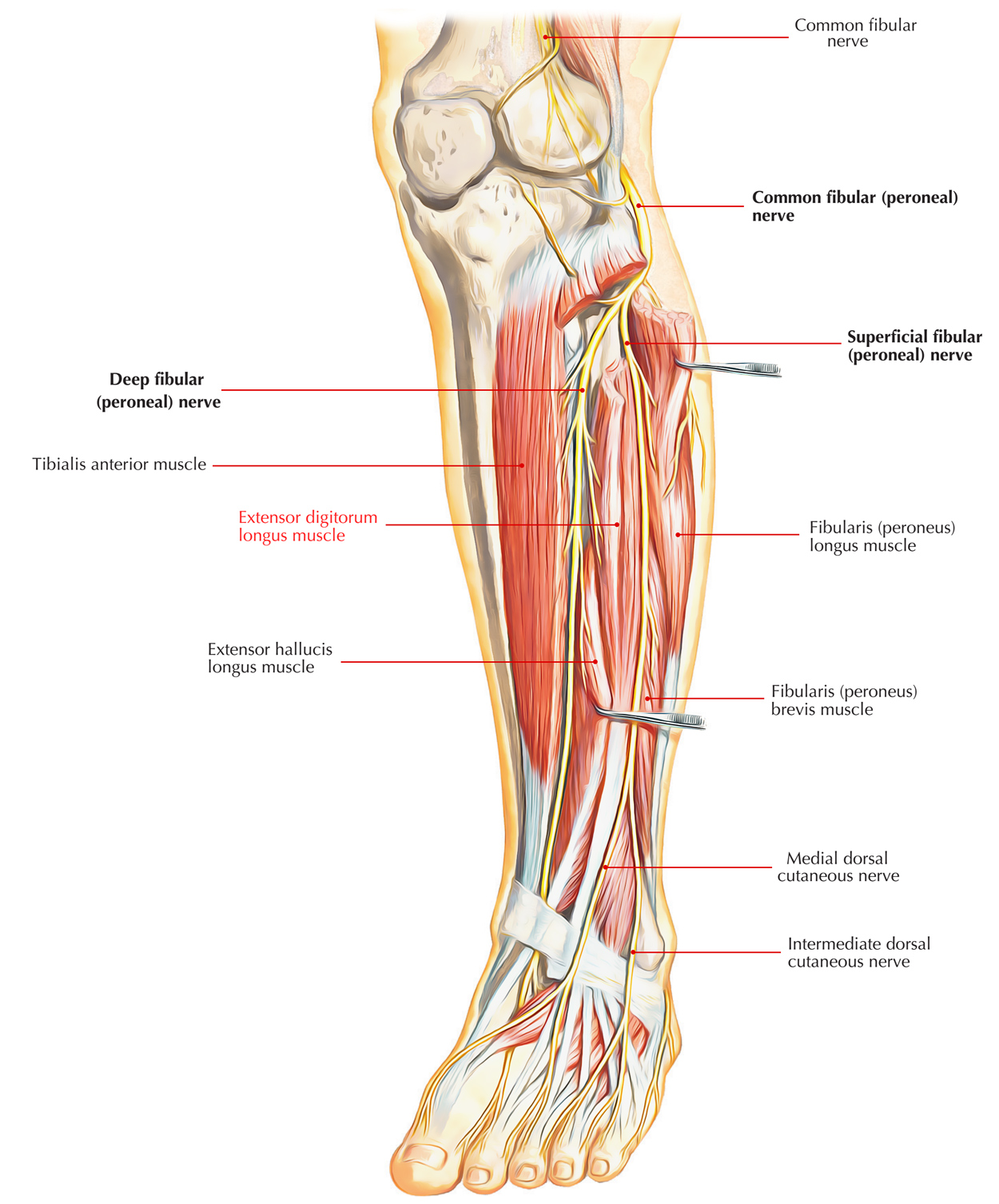
Extensor digitorum Longus emerges generally via the upper half of the medial side of the fibula lateral to and also above the origin of the extensor hallucis longus muscle, as well as prolongs superiorly over the lateral condyle of the tibia. The extensor digitorum longus muscle is the most posterior together with lateral of the muscles in the front compartment of the leg. Just like the tibialis anterior muscle, it also emerges via deep fascia.
Insertion
The extensor digitorum longus muscle comes down to create a tendon, that proceeds inside the dorsal part of the foot, where it splits within four tendons, that enter, by means of dorsal digital growths, within the dorsal sides of the bases of the middle as well as distal phalanges of the lateral four toes.
Extensor Digitorum Longus
Innervation
The extensor digitorum longus muscles get their innervation by means of deep peroneal nerve sections that consist of fibers via the fourth along with fifth lumbar and also first sacral spinal nerves.
Relations
The anterior tibial vessels and also deep fibular nerve lie in between extensor hallucis longus as well as tibialis anterior. Extensor hallucis longus is located laterally to the artery proximally, intercrosses it in the lower third of the leg, along with is medial to it on the foot.
Vascular supply
More distally, the tendon is supplied through the anterior medial malleolar artery along with network, the dorsalis pedis artery, as well as the plantar metatarsal artery of the first digit through piercing sections. Extensor hallucis longus is supplied by the anterior tibial artery through obliquely going branches, along with a variable contribution through the piercing branch of the fibular artery.
Function
The extensor digitorum longus muscles serve as assistants in controlling (decreasing) the decline of the forefoot to the floor immediately going after heel-strike, therefore preventing foot slap.
Throughout the swing stage of gait, it together with the extensor hullucis longus muscle help in offering foot-floor margin. The extensor digitorum longus assists supply pure dorsiflexion of the foot by stabilizing the opposite pull of the tibialis anterior muscle.
Actions
Electrical activation of this muscle triggered extension of the proximal phalanx of every one of the lesser four toes with dorsiflexion, abduction of the foot as well as rise of its lateral border (eversion). Simultaneous electrical activation of the tibialis anterior muscle led to more energetic pure dorsiflexion at the ankle; generally, any propensity for abduction as well as adduction of the foot was cancelled in this test. The extensor digitorum longus strongly prolongs the proximal phalanx of the four lesser toes, and prolongs the middle along with distal phalanges less vitalityously. It also dorsiflexes and everts the foot.
Clinical Significance
Extensor Tendonitis
Extensor tendinitis is inflammation of the extensor tendons which go the top of the foot and also align the toes.
Treatment includes rest, applying of cold treatment throughout the intense phase followed by a complete rehab program consisting of mild extending together with enhancing workouts. Pain is experienced throughout the top of the foot.
Extensor Tendonitis Symptoms
Pain is most likely to happen slowly gradually by excessive use with the professional athlete experiencing a hurting pain on the top of the foot. There might also be some scattered inflammation over the top of the foot. Symptoms of extensor tendonitis include pain on the top of the foot which is worsened throughout running and is eased with rest.
Extensor Digitorum Longus Injury
The harmed Extensor Digitorum Longus Muscle can be cured with a substantial workout routine. Any harm or injury to this muscle might lead to numerous malfunctions like issues along with working out stairs, running, along with playing sports.
A few of the signs that point to a stretched extensor digitorum longus muscle are:
- Pain on the top of the foot and also around the toes
- Issues with raising the foot to any considerable degree.
- Experiencing of feeling numb on the top of the foot.
- Regular cramping of the foot.
- Development of defects like claw toe or hammertoes.

 (53 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)