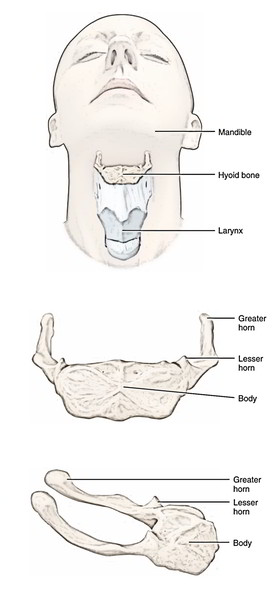
Not really a part of the skull, this U-shaped bone lies in the very front of the neck between the mandible and the larynx in the level of the third cervical vertebra. It’s exceptional in the meaning that, it’s suspended from styloid processes of temporal bones by stylohyoid ligaments and it does not articulate with any bone of the body.
Parts
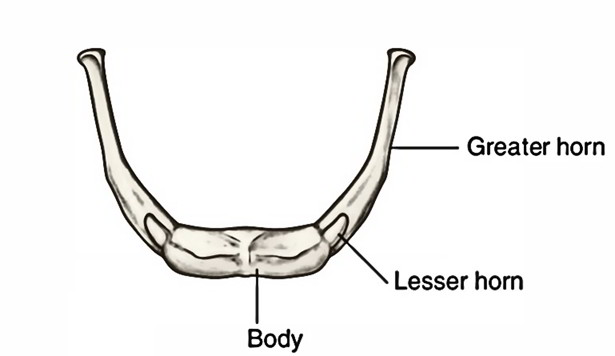
The hyoid bone is made from the following 5 parts:
- A body.
- A pair of greater cornu (or horns).
- A pair of lesser cornu (or horns).
Body
It has elongated and quadrilateral design. The body presents 2 surfaces (anterior and posterior) and 2 lateral extremities:
Its upper part is crossed by a transverse line or ridge and in lots of cases a vertical median ridge divides the body into 2 lateral halves. The anterior surface is convex and faces forwards and upwards.
It faces backwards and downwards. The posterior surface of hyoid bone is divided from the epiglottis by the thyrohyoid membrane; a bursa intervenes between the bone and the membrane. The posterior surface is smooth and concave.
The lateral extremities of the body on every side are constant with the greater cornu. In early life, the lateral extremities are joined with the greater cornu by a cartilage, but after middle life, they become united by a bone.
Greater Cornu
Every greater cornu projects backwards and upwards from the side of the body of the bone. They decrease in size from before backwards. Every cornu finishes posteriorly in a tubercle.
When the neck is loosened, the 2 greater cornua can be grasped in vivo between the index finger and the thumb and after that the hyoid bone can be transferred from side to side.
Lesser Cornu
Every smaller cornu is a small conical bony projection which is connected in the junction of the body and greater cornu. The stylohyoid ligament is connected to the tip of the lesser cornu and is occasionally ossified.
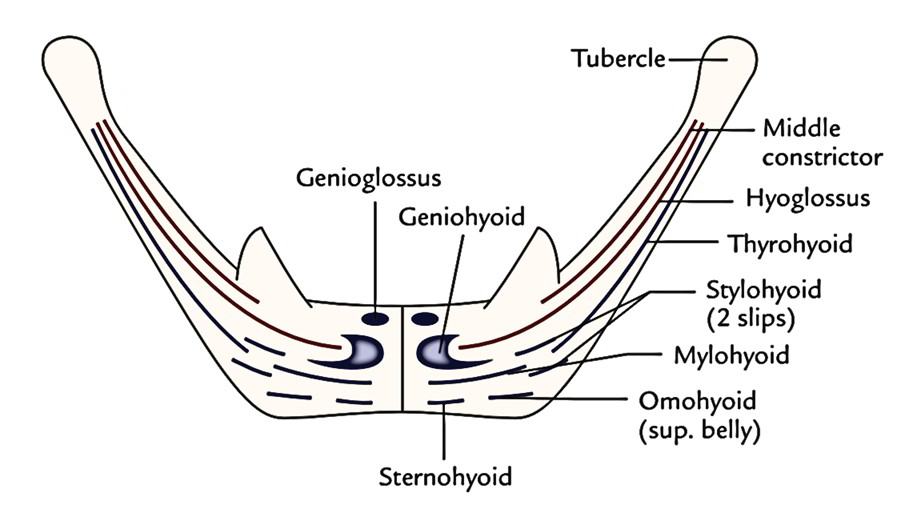
The hyoid bone gives connection to a number of muscles otherwise it’s of little functional importance.
Clinical Significance
In suspected cases of departure, the evaluation of hyoid bone is of great medicolegal value, because fracture of hyoid bone in such cases indicates departure by throttling or strangulation.
The tip of greater cornu can be felt in the relaxed neck near the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle, midway between the laryngeal visibility and mastoid process. The lingual artery creates a loop above the greater cornua; therefore the latter creates an essential surgical landmark for finding the lingual artery for ligation in radical surgery of the neck.

 (49 votes, average: 4.56 out of 5)
(49 votes, average: 4.56 out of 5)