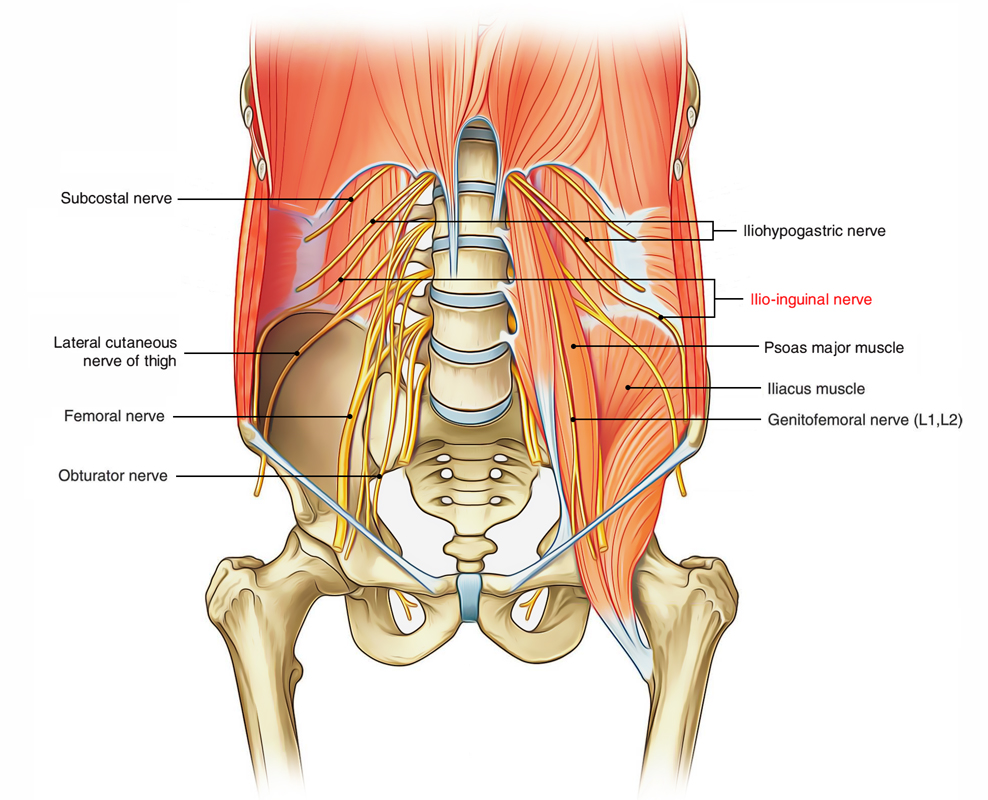
The ilioinguinal nerve is a division of the LI nerve root with a support via T12 in some patients. The nerve goes with a curvilinear course that takes ilioinguinal nerve via its genesis of the LI and sometimes T12 somatic nerves to within the concavity of the ilium.
As the ilioinguinal nerve continues to reach its course medially and inferiorly the nerve might adjoin with the iliohypogastric nerve, where it follows the spermatic cord through the inguinal ring and within the inguinal canal. The division of the sensory innervation of the ilioinguinal nerves differs via person to person since there might be significant overlap with the iliohypogastric nerve.Genesis
The ilioinguinal nerve emerges via the superior part of the lumbar plexus, in the plane in between the transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscles comes down around the abdominal wall, and after that enters the inguinal canal to exit the abdominal wall through the superficial inguinal ring.
Ilioinguinal Nerve
Insertion
- It is the anterior primary ramus of LI spinal nerve.
- It enters the internal oblique muscle via listed below and runs along the inferolateral side of the spermatic cord, and goes into the inguinal canal lateral to the iliohypogastric nerve.
- It emerges through the superficial inguinal ring. It has no lateral cutaneous division.
Functions
Supplies Motor Innervation
- Internal oblique muscles.
- Transversus abdominis muscles.
Sensory Innervation
- The skin on the upper medial element of the thigh.
- Root of penis and scrotum in the male.
- Mons pubis and labium majus in the female.
Clinical Significance
Surgeries
- Ilioinguinal nerve block works in the examination and management of groin pain believed to be subserved by the ilioinguinal nerve, consisting of the pain connected with ilioinguinal neuralgia.
- When integrated with iliohypogastric and genitofemoral nerve block, the method likewise works to supply surgical anesthesia for groin surgery, consisting of inguinal herniorrhaphy.
- Ilioinguinal nerve block with anesthetics can be utilized diagnosti-cally throughout differential neural blockade on an anatomic basis in the examination of groin pain when peripheral nerve entrapment versus lumbar radiculopathy is being examined.
- As a prognostic indicator of the degree of motor and sensory disability, this method works, if damage of the ilioinguinal nerve is being thought about.
Ilioinguinal Neuralgia
In pain in the groin area, is an outcome of damage to the ilioinguinal nerves or genitofemoral nerves along the division of these nerves. This pain is called neuralgia.
Causes
- The common causes consist of injury or damage to the nerves due to surgery carried out in the specific area.
- Tumor or cancer within the abdomen can constrict on these nerves and trigger pain also.
- Damage to the abdominal wall can likewise be a cause.
- Internal issues within the spinal cord which trigger compression on these particular nerve fibers as they originate via the spinal cord.
Symptoms
- Pain in the groin and in the genital area.
- Tingling and changed sensitivity in the area supplied by the nerves.
- Loss of sensitivity in locations such as the inner thigh and genital areas.
- The muscles at the anterior of the abdominal wall might be weak.
Treatment
- Painkillers might not assist manage the symptoms effectively.
- Blocking the nerve signals using a local anesthetic injection can be done.
- Steroid injections might work.
- More recent treatments have actually developed such as pulsed radio frequency, if the above treatment alternatives fail.

 (54 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)
(54 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)