The inferior alveolar nerve a.k.a. the inferior dental nerve is a division of the mandibular nerve, the third division of the trigeminal nerve. The inferior alveolar nerve is primarily a twin motor and sensory nerve. It innervates the lower teeth. It is also the largest branch of the mandibular nerve.
Inferior Alveolar Nerve
Origin
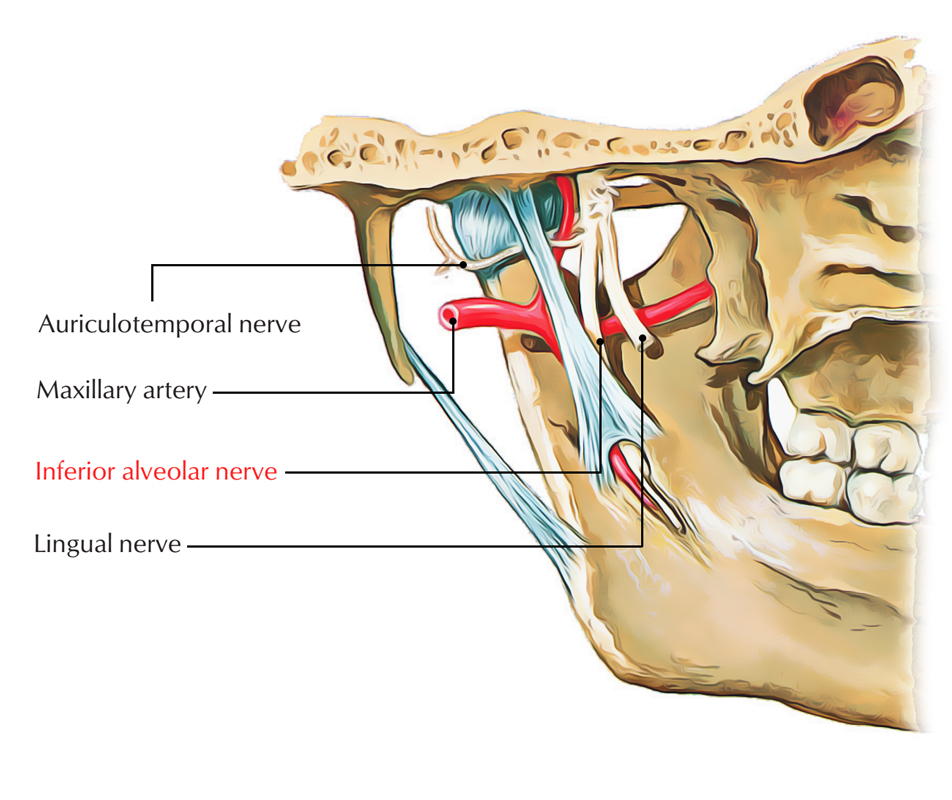
The inferior alveolar nerve arises via the posterior trunk of the mandibular nerve along with the lingual nerve, deep towards the lateral pterygoid muscle.
Origin of Inferior Alveolar Nerve
Course
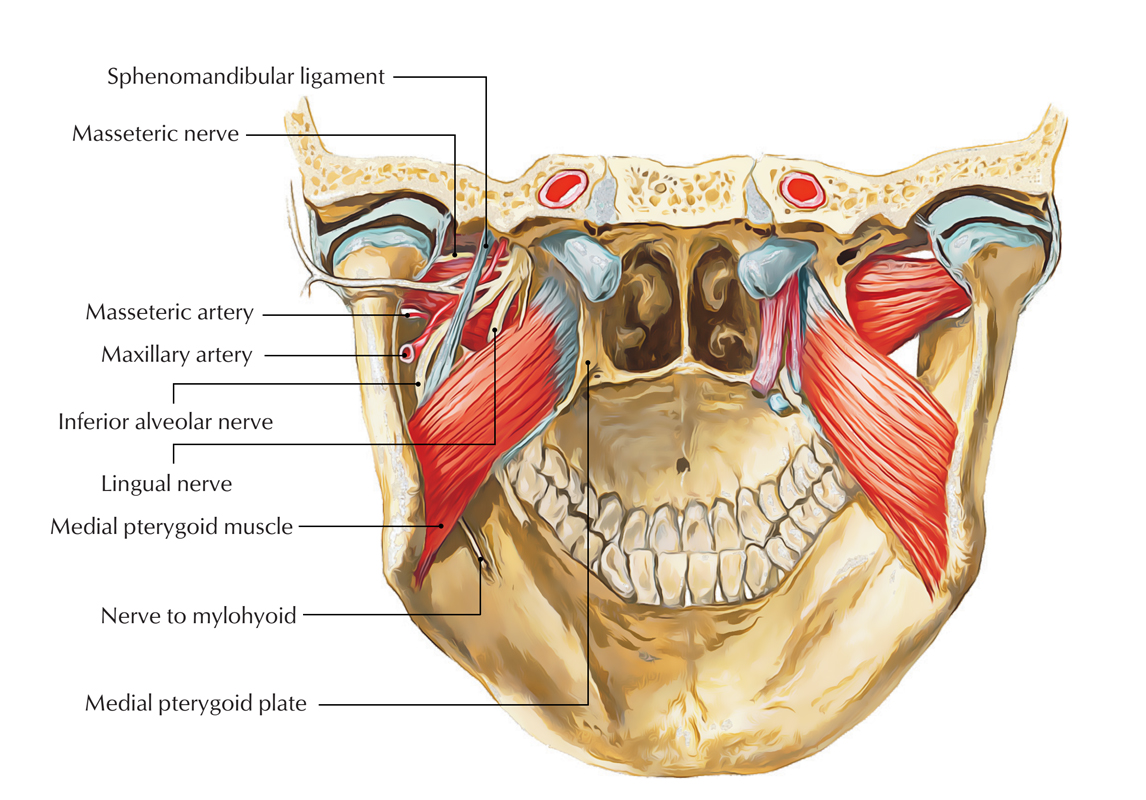
The inferior alveolar nerve is located anterior towards inferior alveolar vessels in the middle of the sphenomandibular ligament along with the ramus of the mandible.
After arising inferior towards the lower head of the lateral pterygoid, it travels on the medial pterygoid perpendicularly inferiorly and anteriorly. It afterwards goes inside the mandibular foramen along with inferior alveolar artery, crosses the mandibular canal till mental foramen and ends by separating in mental and incisive branches.
Course of Inferior Alveolar Nerve
Branches
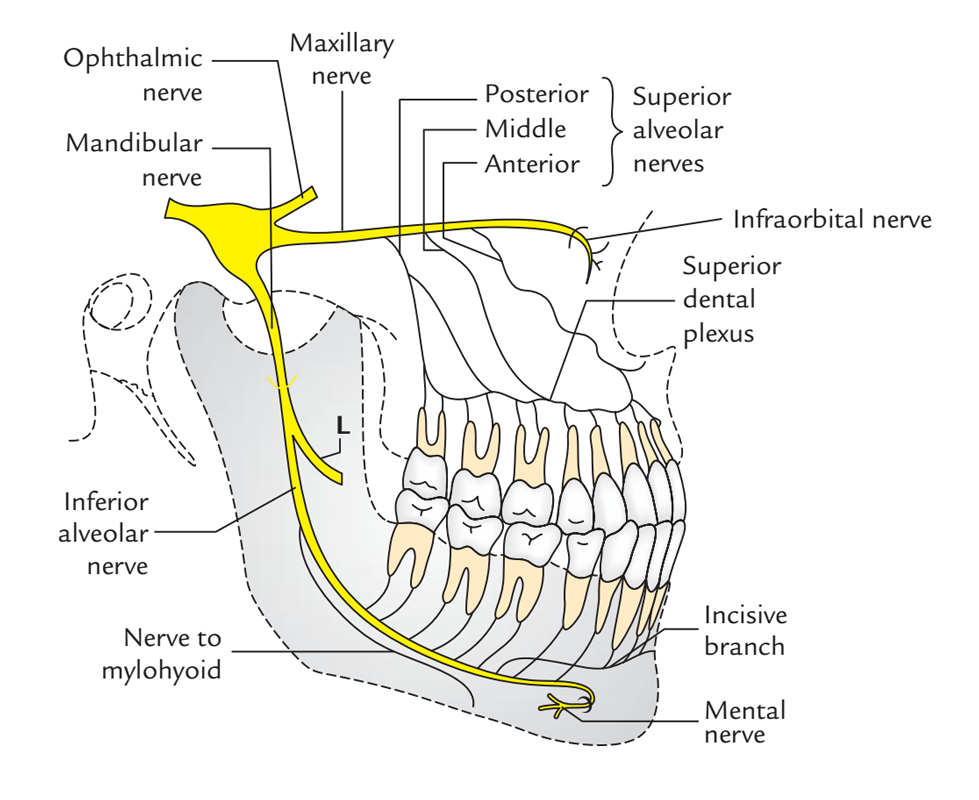
- Nerve towards mylohyoid arises via the inferior alveolar nerve prior to its entrance inside the mandibular canal. In order to connect with the mylohyoid groove, it perforates the sphenomandibular ligament. Mylohyoid and anterior belly of digastric muscle are innervated by it.
- Dental branches innervate molar as well as premolar teeth.
- Mental nerve arises out through mental foramen in order to innervate:
- Skin of the chin.
- Skin and mucus membrane of the lower lip.
- Incisive branch innervates canine and incisor teeth.
Innervation
- Along with all lower teeth and most of the related gingivae, the mucosa along with skin of the lower lip and skin of the chin are also innervated by it.
- The mylohyoid muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle are innervated by its motor branch.
Clinical Significance
Inferior alveolar nerve block/inferior alveolar block/1A block
In order to execute dental procedures on the mandibular teeth, it is the most common nerve block executed in dentistry. The anesthetic agent is injected within the mandibular foramen being projected by the lingual, a little superior towards the entrance of inferior alveolar nerve.
If needle is inserted too far posteriorly, it may enter the parotid gland as well as harm the facial nerve causing transient facial palsy, while executing inferior alveolar nerve block so, special care must be taken in order to not overdo the insertion.
Injuries during Surgery
Reasons of inferior alveolar nerve damage consist of:
- Local anesthetic injections
- Third molar surgery
- Ablative surgery
- Orthognathic surgery
- Endodontics
- Trauma
- Implants
The inferior alveolar nerve neuropathy associated with third molar surgery or inferior alveolar block injections is generally short-termed; however can continue and become permanent around 3 months.
Root canal Complication
During the time when root canal therapy is done on mandibular teeth posterior towards the mental foramen, injury to the inferior alveolar nerve may usually happen.
Mostly it can be an entirely mechanical injury involving tools via the apex of the tooth; however, it appears often as a physicochemical injury via the sealant going to the inferior alveolar nerve.
At least till they set, all sealants currently used can be neurotoxic. If they infiltrate the epineurium and encounter the fascicles, they can cause physicochemical damage to the inferior alveolar nerve.

 (57 votes, average: 4.86 out of 5)
(57 votes, average: 4.86 out of 5)