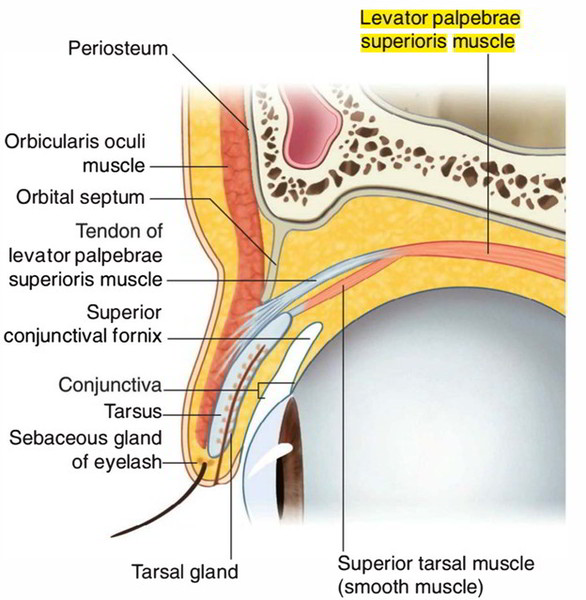
This muscle is an eye opener (pun intended). The levator palpebrae superioris muscle attaches into the tarsal plate and skin of the upper eyelid and is the primary elevator of the eyelid. Weakness in this muscle results in ptosis (drooping) of the upper eyelid and may reflect a problem with the oculomotor nerve. The oculomotor nerve provides the motor control for the levator palpebrae superioris and most (4 of 6) of the extraocular muscles. The levator palpebrae superioris is assisted by the superior tarsal muscle, a thin smooth muscle sheet in the upper eyelid innervated by sympathetic fibers.
Levator palpebrae superioris raises the upper eyelid. It is the most superior muscle in the orbit, originating from the roof. Its primary point of insertion is into the anterior surface of the superior tarsus, but a few fibers also attach to the skin of the upper eyelid and the superior conjunctival fornix.
Contraction of the levator palpebrae superioris raises the upper eyelid.
A unique feature of the levator palpebrae superioris is that a collection of smooth muscle fibers passes from its inferior surface to the upper edge of the superior tarsus. This group of smooth muscle fibers (the superior tarsal muscle) help maintain eyelid elevation and are innervated by postganglionic sympathetic fibers from the superior cervical ganglion.
Loss of oculomotor nerve function results in complete ptosis or drooping of the superior eyelid, whereas loss
of sympathetic innervation to the superior tarsal muscle results in partial ptosis.
Origin
- Inferior surface of the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone.
- Orbital surface of the body of the sphenoid bone anterior to the optic foramen.
Insertion
It expands towards the upper eyelid and divides into superficial and deep layers.
They are inserted to:
- Orbital septum Palpebral ligaments (medial and lateral)
- Superior tarsal plate
- Skin of the upper eyelid.
The smooth muscle fibres of the levator palpebrae superioris is called as Muller’s muscle
The aponeurosis of this muscle divides the lacrimal gland into palpebral and orbital parts.
Nerve supply
- Upper division of the oculomotor nerve.
- Sympathetic fibres from segment of the spinal cord supplies the smooth muscle fibres of the muscle.
Actions
It opposes the action of the orbicularis oculi. So it elevates the upper eyelid. Paralysis of the muscle causes ptosis (drooping of the upper eyelid). Paralysis of the smooth muscle fibres of this muscle causes pseudo ptosis. (Horner’s syndrome)
The levator palpebrae superioris attaches from the sphenoid bone superiorly, to the upper eyelid interiorly. When the levator palpebrae superioris contracts, it pulls the upper eyelid superiorly toward the sphenoid bone. Therefore the levator palpebrae superioris elevates the upper eyelid.
Test Your Knowledge
Levator Palpebrae Superioris

 (55 votes, average: 4.86 out of 5)
(55 votes, average: 4.86 out of 5)