Mylohyoid or Mylohyoideus muscle is located deep towards the anterior belly of the digastric muscle and it is a plane, triangle-shaped muscle. In order to form the canal-like floor of the mouth, the right and left mylohyoid muscles connect in the median fibrous raphe. The floor of the mouth is also known as diaphragma oris because the tongue is located over floor of the mouth.
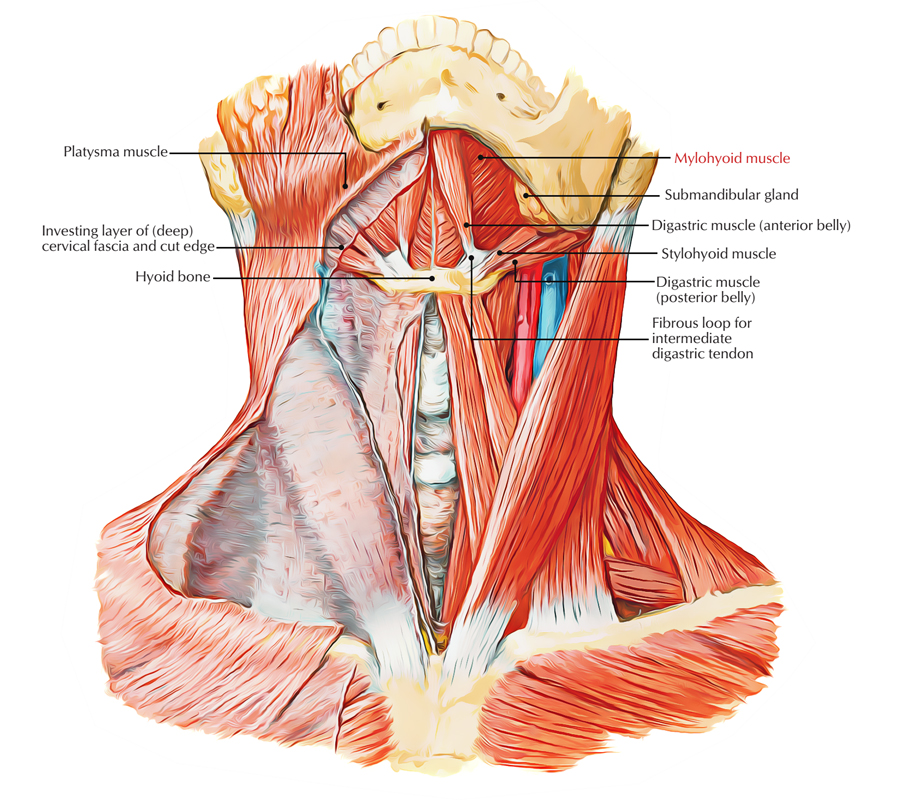
Mylohyoid Muscle
Origin
There are two Mylohyoid or Mylohyoideus muscles (left and right) which arise from the mandible at the mylohyoid line, which spreads out in front from the mandibular symphysis up to the back of the last molar tooth.
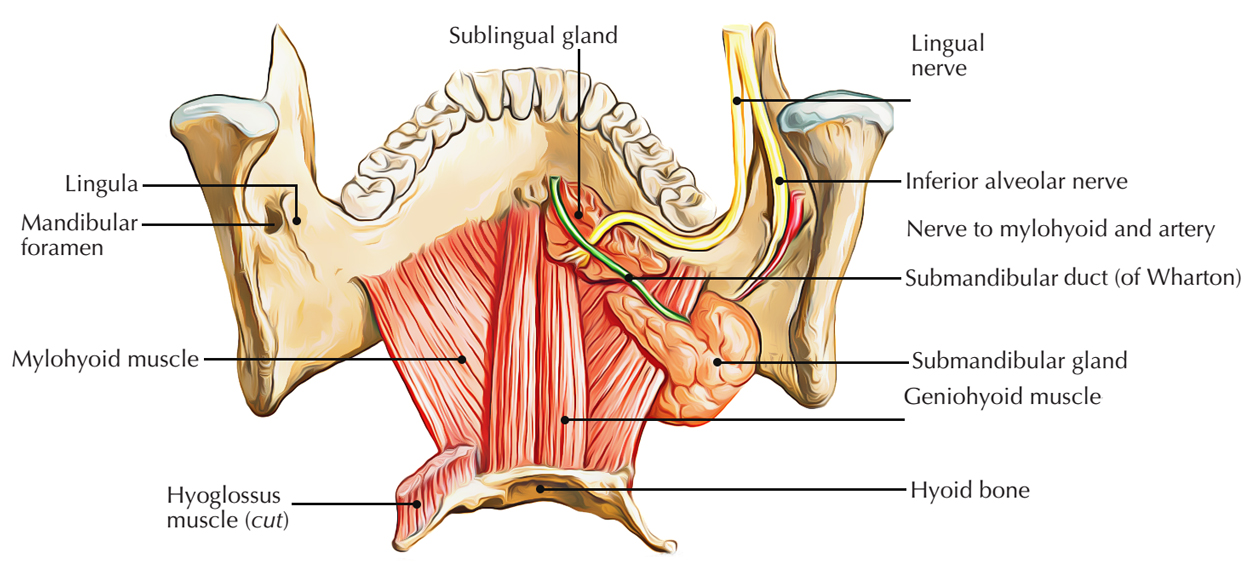
Mylohyoid Muscle
Insertion
It is a pharyngeal muscle which is originated from the first pharyngeal arch and it is categorized among the suprahyoid muscles. Fibres of this muscle travel downwards as well as medially.
- The posterior fibres attach in the body of the hyoid bone.
- The middle and anterior fibres spread out from symphysis menti to the hyoid bone and attach in the median fibrous raphe.
Nerve supply
The mylohyoid muscle is supplied by mylohyoid nerve, which is a branch of inferior alveolar nerve from mandibular nerve; because it emerges from the first pharyngeal arch.
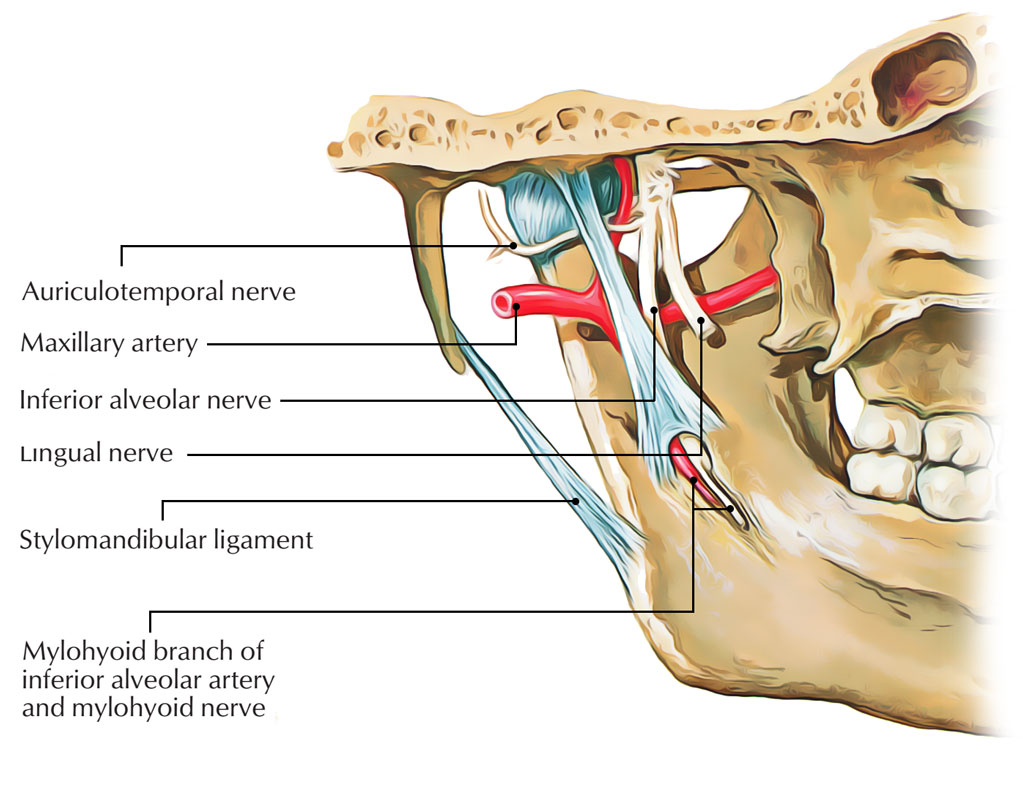
Mylohyoid Nerve Supply
Actions
- The mylohyoid muscle raises the floor of the mouth and the tongue, which helps in speaking and swallowing.
- Depression of the mandible against resistance, if hyoid is kept fixed.
- It fixes or elevates the hyoid bone.
- Reinforces floor of the mouth.
Variations
- The mylohyoid may be united to or substituted by the anterior belly of the digastric muscle;
- Additional bands to other hyoid muscles are frequent.
- Sometimes, the fibers of the left and right muscles are constant whenever median raphe is absent.
Clinical Significance
Mylohyoid boutonnière
Mylohyoid or mylohyoideus muscle defects are very common. Through the defects inside the submandibular space, the constituents of the sublingual space may herniate creating a cervical mass. The herniated tissue can be exposed more by making the patient to swallow, if it is diagnosed on ultrasound. The herniated tissue can be made up of fat, vessels or parts of the sublingual gland.

 (49 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)
(49 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)