Shape
When viewed from above the skull is usually oval in shape. It is wider posteriorly than anteriorly. The shape may be more nearly circular.
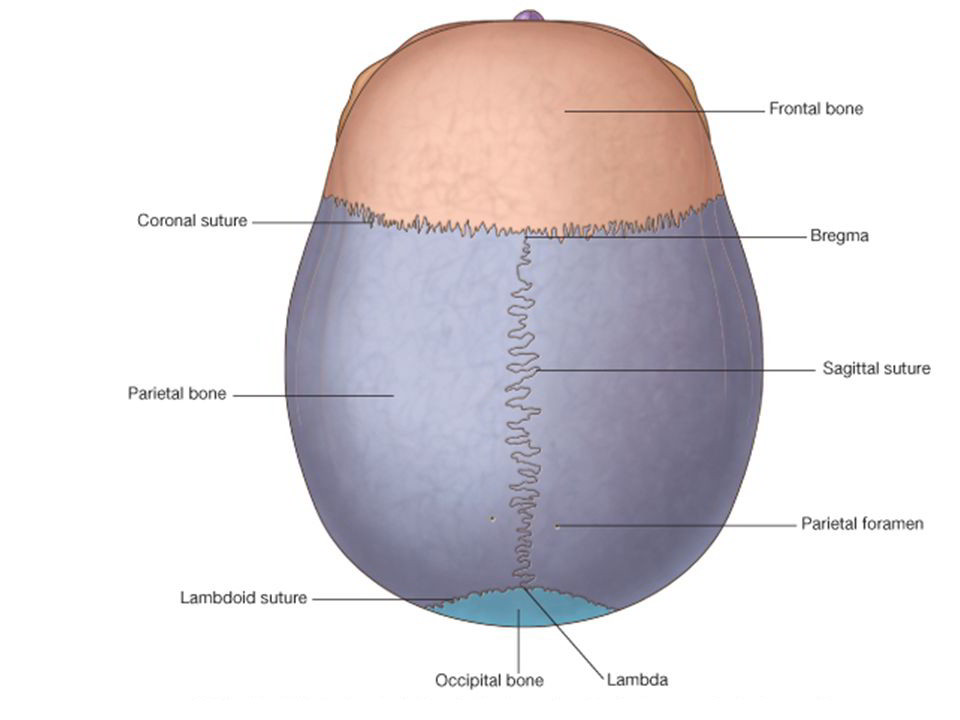
Bones Seen in Norma Verticalis
- Upper part of the frontal bone anteriorly.
- Uppermost part of the occipital bone posteriorly.
- parietal bone on each side.
Sutures
1. Coronal suture. This is placed between the frontal bone and the two parietal bones. The suture crosses the cranial vault from side to side and runs downwards and forwards.
2. Sagittal suture.It is placed in the median plane between the two parietal bones.
3.Lambdoid suture. It lies posteriorly between th occipital and the two parietal bones, and it run downwards and forwards across the cranial vault.
4. Metopic suture. This is occasionally present in about 3 to 8% individuals. It lies in the median plane and separates the two halves of the frontal bone.
Some other Named Features
1. The vertex is the highest point on the sagittal suture.
2. The vault of the skull is the arched roof for the dome of the skull.
3. The bregma is the meeting point between the coronal and sagittal sutures. In the foetal skull, this is the site of a membranous gap, called the anterior fontanelle, which closes at eighteen month of age.
4. The lambda is the meeting point between the sagittal and lambdoid sutures. In the foetal skull, this is the site of the posterior fontanelle which closes at two to three months of age.
5. The parietal tuber (eminence) is the area of maximum convexity of the parietal bone. This is a common site of fracture of the skull.5. The parietal tuber (eminence) is the area of maximum convexity of the parietal bone. This is a common site of fracture of the skull.
6. The parietal foramen, one on each side, pierces the parietal bone near its upper border, 2.5 to 4 cm in front of the lambda. The parietal foramen transmits an emissary vein from the veins of scalp into the superior sagittal sinus.
7. The obelion is the point on the sagittal suture between the two parietal foramina.
8. The temporal lines begin at the zygomatic process of the frontal bone, arch backwards and upwards, and cross the frontal bone, the coronal suture and the parietal bone. Over the parietal bone there are two lines, superior and inferior. Traced anteriorly, they fuse to form a single line. Traced posteriorly, the superior line fades out over the posterior part of the parietal bone, but the inferior temporal line continues downwards and forwards.

 (52 votes, average: 4.67 out of 5)
(52 votes, average: 4.67 out of 5)