Olfactory Nerve is the only sensory and carries the sense of smell from nasal cavity. It is the 1st cranial nerve and is the shortest of all the pairs of cranial nerves.
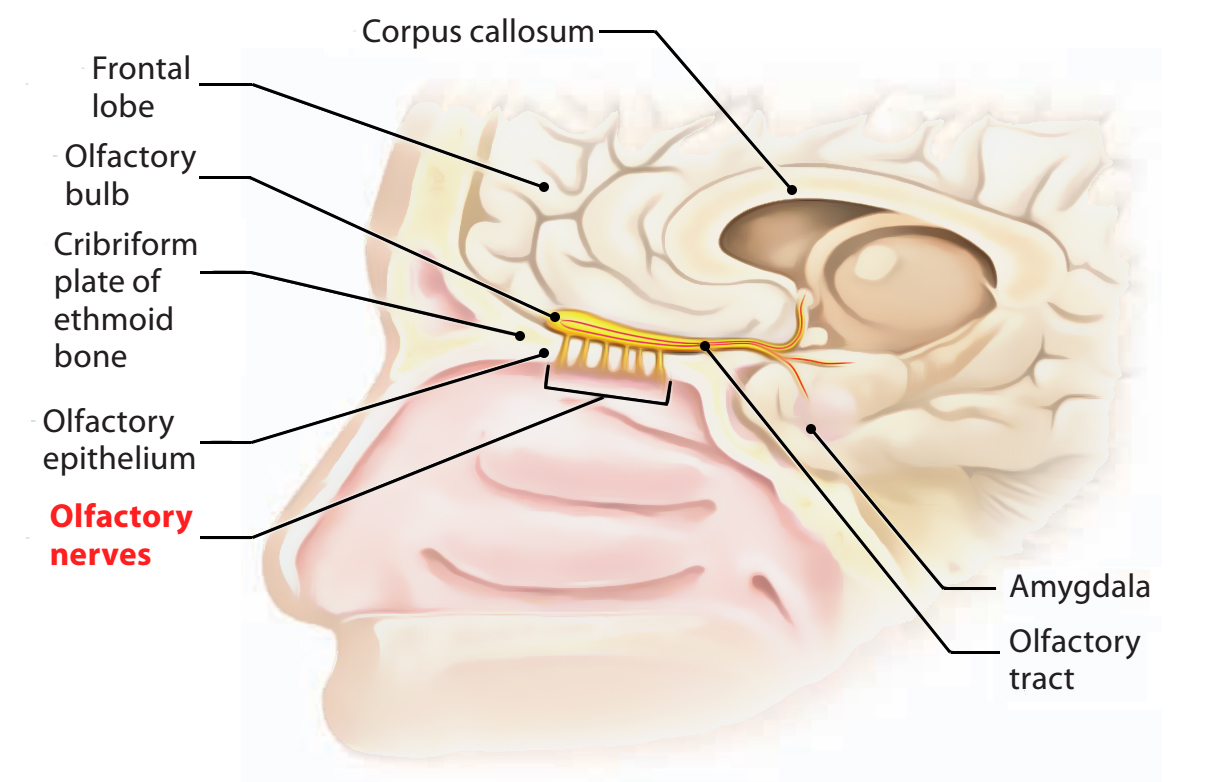
Olfactory Nerves
Unique Features
The primary sensory neurons of olfactory nerve (olfactory neurons) go through constant turnover, i.e they’re constantly replaced by stem cells in the olfactory neuroepithelium.
The primary sensory neurons of olfactory nerve, located on the body surface in the epithelial lining of the nasal cavity and their dendrites is located free in the mucous film.
Functional Parts
Specific sensations of smell from the olfactory region of the nasal cavity are carried by special somatic afferent fibres and terminate in the olfactory bulb.
Course, Relationships and Distribution
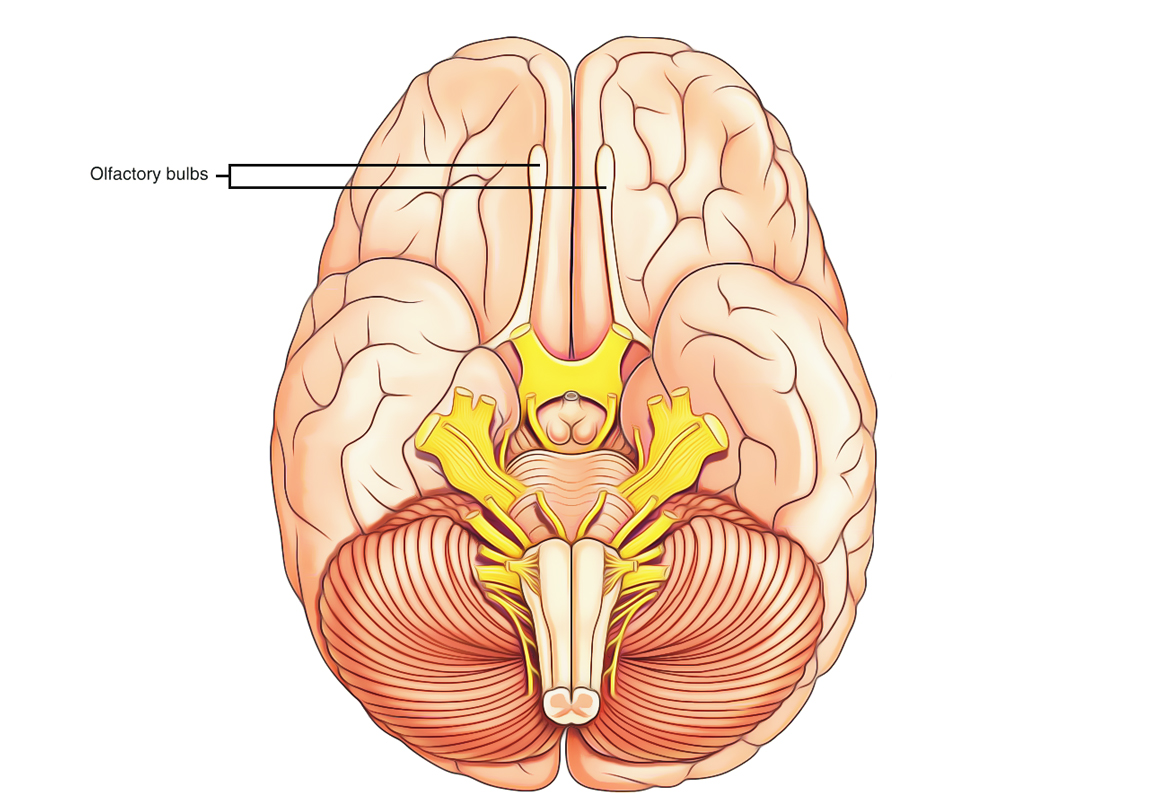
Olfactory Bulbs
Every olfactory nerve contains about 20 tiny bundles of non-myelinated nerve fibres. In the olfactory bulb, they synapse with all the mitral cells.
They originate from primary receptor neurons (changed bipolar neurons) of the olfactory epithelium of nasal cavity and go through foramina in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid to goes into the anterior cranial fossa, where they terminate in the olfactory bulb (The olfactory bulbs originate from the cerebrum).
Three meninges surround the bundles of olfactory nerves (specifically pia mater, arachnoid mater and dura mater) near the cribriform plate. This gives a potential communication between the subarachnoid space and lymphatics of the nasal mucosa. Hence, infection from nose can propagate into the meninges of the brain.
Distribution: olfactory region of the nasal cavity.
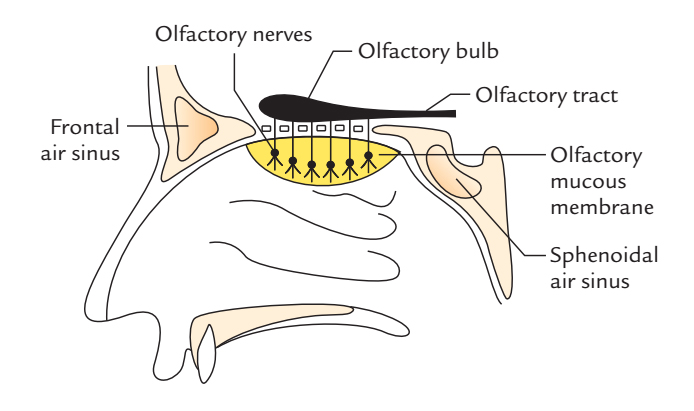
Olfactory Nerve: Course, Origin and Distribution
Clinical Significance
Anosmia
The loss of sense of smell is referred to as anosmia. Anosmia can happen for a number of motives like atrophic rhinitis (degenerative disorder of nasal mucosa), fracture of the anterior cranial fossa (ethmoidal fracture), etc. The ethmoidal fracture is frequently related to blood-stained cerebrospinal fluid (CSF rhinorrhea).
Clinical Testing of Olfactory Nerve
The olfactory nerve is analyzed medically by requesting the patient to smell common scents like peppermint, garlic, or cloves from every side of his nostril individually with eyes closed.

 (53 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)