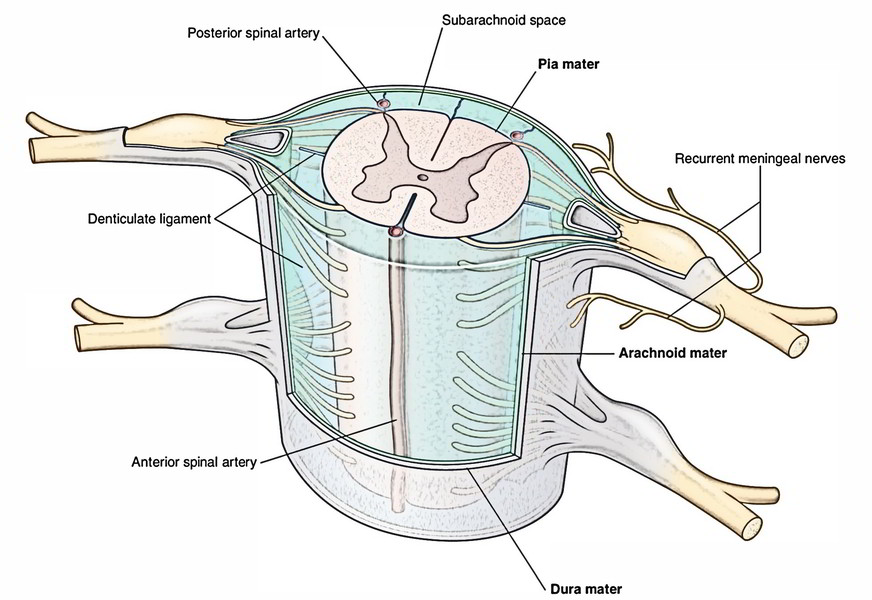
The spinal cord is surrounded by 3 coverings referred to as meninges. From superficial to deep, all these are as follows:
- Spinal dura mater.
- Spinal arachnoid mater.
- Spinal pia mater.
The subdural space is potential space between the dura and arachnoid maters while subarachnoid space is the large space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater.
Spinal Dura Mater
It goes from foramen magnum to the lower border of S2 vertebra and the prolongation of the inner meningeal layer of cranial dura mater. On the body of axis vertebra it is connected securely to the foramen magnum, the tectorial membrane and the posterior longitudinal ligament. Elsewhere it is located free in the vertebral canal. The lower blind end of dural tube is pierced by filumterminale in its centre.
The spinal dura is pierced segmentally by dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal nerves and prolonged over these roots as sleeve-like projections, which goes into the intervertebral foramina and ends by fusing with the epineurium of the spinal nerves. The recurrent meningeal branches of the spinal nerves supply the spinal dura.
Subdural Space
It’s a potential space between the spinal dura and arachnoid mater consisting of a thin film of serous fluid, which functions as a lubricant. As a consequence, the dura mater can freely move over the arachnoid. The subdural space is.
Spinal Arachnoid Mater
It’s a thin translucent vascular membrane that loosely invests the spinal cord. Above it’s constant with the arachnoid mater enclosing the brain and below it goes up to the lower border of second sacral vertebra. It’s divided from pia mater by the subarachnoid space. The arachnoid mater sends many fine thread like processes across the subarachnoid space to the pia mater creating a spider’s web like arrangement.
Subarachnoid Space
The subarachnoid space is a comparatively large space between arachnoid mater and pia mater. It’s filled up with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which creates about half of the entire volume of CSF (i.e., 75 ml out of 150 ml). It interacts with all the subarachnoid space around the brain in the foramen magnum. Below the level of conus medullar is (lower conical end of spinal cord) the space is very roomy (referred to as lumbar cistern) and includes only caudaequina and filumterminale in a pool of CSF. The lumbar puncture is generally done in this region between the L3 and L4 vertebra.
Spinal Pia Mater
It’s a vascular membrane that closely invests the spinal cord. The pia mater is altered at some locations. These adjustments are referred to as processes of pia mater.
Processes of Pia Mater
Filumterminale: It’s a fine thin thread like prolongation of pia mater beyond the conusmedullaris. It’s about 20 cm long and goes from tip of conusmedullaris to the base of the coccyx. It pierces the dural tube, goes through the sacral canal and sacral hiatus to obtain connection on the dorsum of the very first section of the coccyx. The filumterminale is split into 2 parts: filumterminaleinternum and filumterminaleexternum.
The filumterminaleinternum is about 15 cm long and is located inside the dural sac.
The filumterminaleexternum is 5 cm long and is located outside the dura mater.
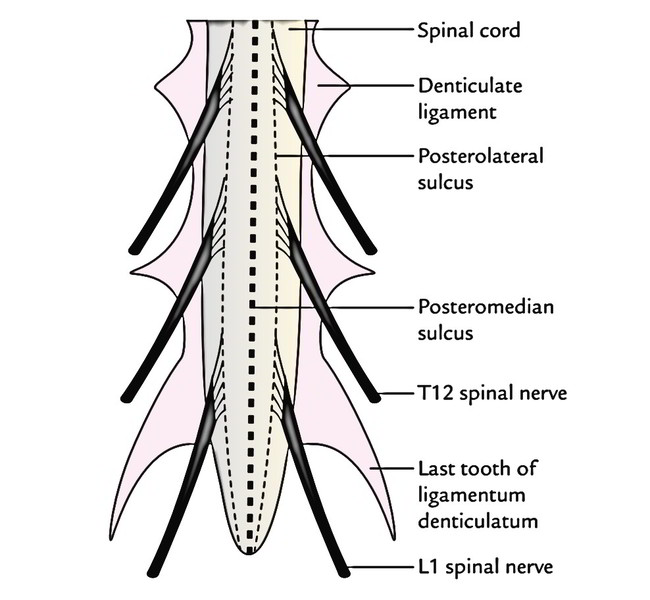
Ligamentadenticulata: On every side between the dorsal and ventral nerve roots, the pia mater creates narrow ribbon like translucent bands named ligamentadenticulata. The lateral margin of every ligamentumdenticulatum sends 21 teeth-like projections, which go through subarachnoid space and arachnoid mater to obtain connection on the inner surface of the dural tube between the points of development of 2 adjacent spinal nerves. Consequently ligamentadenticulata helps to anchor the spinal cord in the middle of the subarachnoid space. The very first tooth of ligamentumdenticulatum is right at the level of the foramen magnum, while the last tooth is located between T12 and L1 spinal nerves.
Linea splendens: It’s a thickened band of pia mater along the anterior median fissure of the spinal cord.
Subarachnoid septum: It’s a fenestrated pial septum in the midsagittal plane, which attaches the pia mater with arachnoid mater posteriorly. Posteriorly, the pia mater is also connected to the posterior median septum of the spinal cord.
Clinical Significance
Lumbar Puncture
The lumbar puncture is done to draw CSF from subarachnoid space for diagnostic and curative goals. The needle is inserted between L3 and L4 or L4 and L5 vertebrae with patient’s back bent either in sitting position or being located on a bed in left lateral position, generally the afterwards when patient is curled up being located on left side. The needle goes through the supraspinous and interspinous ligaments and between ligamentaflava before piercing the dura mater. As the dura mater is pierced, there’s a distinctive feel of give way. Since the spinal cord ends at the lower border of L1 vertebra, there isn’t any risk of damage to the spinal cord.
Spinal Anesthesia
To give spinal anesthesia, the anesthetic solution is injected into the subarachnoid space. It mixes up with CSF surrounding the spinal nerve roots which get anesthetized. The process is same as that of lumbar puncture.
Epidural Anesthesia
To give epidural anesthesia, the anesthetic solution is injected into the epidural space in the desired site without piercing the dura mater. The solution infiltrates via the meningeal sheaths around the nerve roots, which hence get anesthetized.

 (58 votes, average: 4.90 out of 5)
(58 votes, average: 4.90 out of 5)