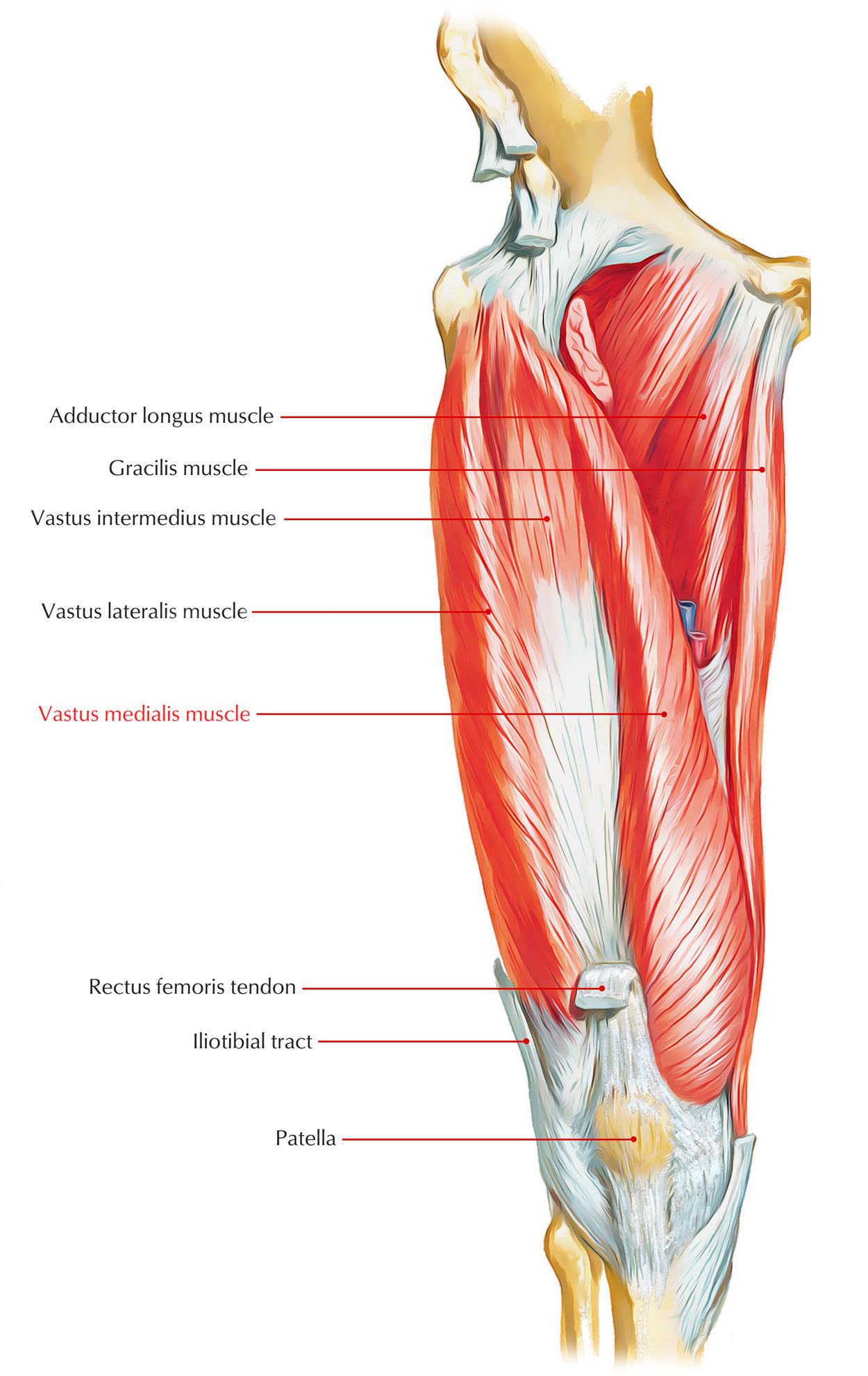
The vastus medialis is an extensor muscle located medially in the thigh that extends the knee. The vastus medialis is present in the anterior compartment of thigh, and is among the four muscles that comprise the quadriceps muscle. The various other are the vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius as well as rectus femoris.It is the most medial of the “vastus” set of muscles.
Vastus Medialis Muscle
Attachments
The vastus medialis connects proximally along the whole overall length of the posteromedial element of the shaft of the femur, to the lower half of the intertrochanteric line, the medial lip of the linea aspera, the upper portion of the medial supracondylar line, the tendons of the adductor longus as well as adductor magnus, and also to the medial intermuscular septum.
Anteriorly, the vastus medialis attaches to the aponeurosis of the quadriceps femoris tendon together with the vastus intermedius muscle, and its fibers twist around the femur angling downward via its posterior connections. Therefore, the instant the muscle is released anteriorly and also pulled aside, one sees a considerable area of bare bone in between it and also the vastus intermedius. This distinguishes with the substantial lateral attachment of the vastus intermedius to the anterior femur which underlies much of the vastus lateralis.
The vastus medialis connects distally not just to the medial border of the patella and through the patellar ligament to the tibial tuberosity, however also, through a strip of muscle to the medial patellar retinaculum. The distal fibers of the vastus medialis are noticeably angulated when they attach around the patella as well as can be plainly separated via the remainder of the vastus medialis by fiber direction and by a fascial plane.
These distal angulated fibers frequently connect proximally not to the femur, however mainly to the adductor magnus, partially to the adductor longus, and to the medial intermuscular septum. The latter obliquely aligned fibers have actually been defined the vastus medialis oblique.
Insertion
Medial quadriceps tendon to patella and also straight inside medial patella, through ligamentum patellae into tubercle of tibia
Action
- Extends knee
- Supports patella
Structure
- The vastus medialis occurs medially along the whole length of the femur, and connects with the other muscles of the quadriceps in the quadriceps tendon.
- The vastus medialis muscle stems along nearly the whole length of the shaft of the femur (on the back of the shaft), travel down the within the thigh to connect to the medial element of the patella bone.
- The vastus medialis muscle stems via a constant line of connection on the femur, which starts on the front along with middle side (anteromedially) on the intertrochanteric line of the femur.
- It proceeds down as well as back (posteroinferiorly) around the pectineal line and after that comes down around the inner (medial) lip of the linea aspera and over the medial supracondylar line of the femur.
- The fibers assemble over the inner (medial) part of the quadriceps tendon and also the inner (medial) border of the patella.
- The obliqus genus muscle is the most distal section of the vastus medialis muscle. Its specific training plays an essential function in preserving patella position and restricting injuries to the knee. Without any clear delineation, it is just the most distal group of fibers of the vastus medialis.
Clinical Significance
Pain and Symptoms Related to the Vastus Medialis
Pain on the within the knee extending half method up the front of the thigh.
Consistent pain in the knee joint.
Can trigger the knee to ‘buckle’ (technique knee).
Individuals frequently sleep with a pillow in between the knees to ease the pain.

 (56 votes, average: 4.76 out of 5)
(56 votes, average: 4.76 out of 5)