Great Saphenous Vein
The Great Saphenous Vein is located in the superficial fascia and is easily observed (Greek saphenous = easily viewed). The great saphenous vein is the longest vein of the body and represents the pre-axial vein of the lower limb. It’s also termed long saphenous vein.
Course
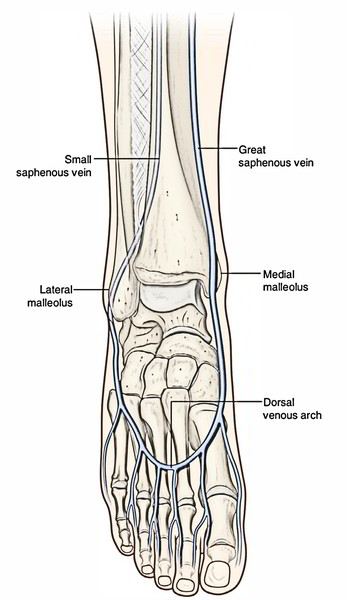
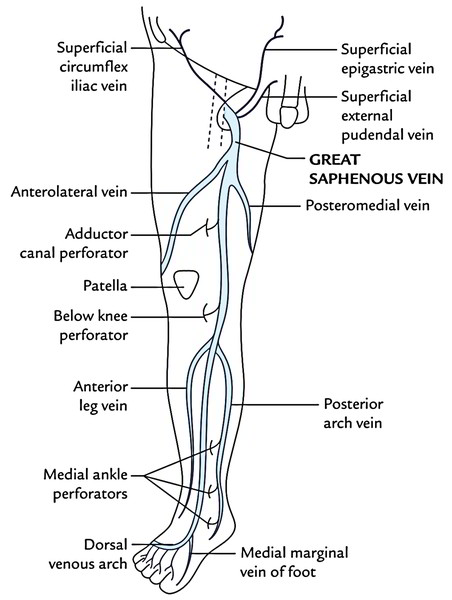
It’s created on the dorsum of foot by the union of the medial end of the dorsal venous arch of the foot and medial marginal vein of the foot. The vein runs upward about 2.5 cm in front of the medial malleolus, crosses obliquely the medial surface of the lower third of tibia, and after that ascends a little behind the medial border of tibia to reach the knee, where it is located on the posteromedial aspect of the knee joint, about 1 handbreadth posterior to the patella; from here it runs upward along the medial side of the thigh to reach the saphenous opening (fossa ovalis).
It goes through the saphenous opening after piercing the cribriform fascia and drains into the femoral vein after piercing the femoral sheath.
Tributaries
- At the commencement: Medial marginal vein of the big toe.
- In the leg:
1. Conveying veins between small saphenous and deep veins.
2. Posterior arch vein. It’s pretty large and continuous. It accumulates the blood from the posteromedial aspect of the calf and starts of a series of small venous arches attaching the 3 medial ankle-perforating veins (perforators). - Just below the knee:
1. Anterior veins of the leg. They go diagonally (upward, forwards, and medially) across the shin and join the great saphenous vein.
2. A couple of veins from the calf which interacts with all the small saphenous vein. - In the thigh:
1. Anterolateral vein. It commences in the lower part of the front of thigh, crosses the apex of femoral triangle, and joins the great saphenous vein in the upper part of the thigh.
2. Posteromedial vein (accessory saphenous vein). It commences from the posteromedial aspects of the thigh and joins with all the great saphenous vein; occasionally it might convey below with the small saphenous vein. - Just before piercing the cribriform fascia:
1. Superficial epigastric vein.
2. Superficial circumflex iliac vein.
3. Superficial external pudendal vein.
These veins accompany the corresponding superficial branches of the femoral artery. - Just before the conclusion in the femoral vein: Deep external pudendal vein (last tributary) empties the blood from the anterior part of the perineum.
Thoraco-epigastric vein: It runs along the anterolateral wall of the trunk. It attaches the superficial epigastric vein with the lateral thoracic vein. So, it creates an essential communication between the femoral and axillary veins (i.e., upper and lower limbs).
Valves In The Great Saphenous Vein
There are around 10 to 20 valves in the great saphenous vein, outside of which the location of 2 needs special mention here: (a) 1, which is located just before it pierces the cribriform fascia and (b) the other, which is located at its junction together with the femoral vein (saphenofemoral valve). The saphenofemoral valve is of great functional importance. It is located about 3.5 to 4 cm inferolateral to the pubic tubercle. In about 80% people, the external iliac vein possesses a valve, which shields the saphenofemoral valve against high venous pressure. The remaining 20% cases who don’t have this valve become the casualty of high venous pressure and develop varicose vein, which commences at the saphenofemoral junction and slowly stretches downward.
Surface Mark of The Great Saphenous Vein
- At ankle, it is located 2.5 cm anterior to the medial malleolus.
- In leg, it ascends by crossing the medial surface and medial border of the tibia.
- At knee, it is located about a hand’s width posterior to the medial margin of the patella.
In thigh, it ascends obliquely on the medial aspect of the thigh to reach a stage 3.5-4 cm inferolateral to the pubic tubercle (saphenofemoral junction).
Clinical Significance
- Venesection of the great saphenous vein: The great saphenous vein in front of medial malleolus at ankle is the most favored site of venesection (cut-down) in crisis scenario when the superficial veins elsewhere in the body are collapsed and imperceptible, to add the canula for protracted administration of intravenous fluids.
Notice that, in front of medial malleolus, saphenous nerve is located in front of the vein. Thus, during cut-down process, the saphenous nerve ought to be recognized to avert its injury. - Great saphenous vein graft: In coronary by pass surgery to ease the ischemia of the heart, a section of great saphenous vein is removed and utilized for aortocoronary grafting to by pass an arterial obstruction. Because of the presence of valves, the vein must be reversed so that its valves don’t obstruct the blood circulation.
Small (Short) Saphenous Vein
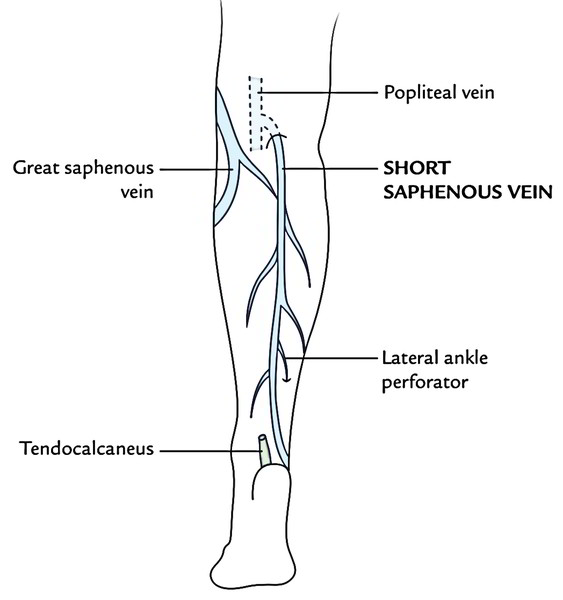
It’s created below and behind the lateral malleolus by the union of the lateral end of the dorsal venous arch, and the lateral dorsal digital vein of the little toe. It runs upward behind the lateral malleolus, along the lateral border of tendocalcaneus, and is escorted by the sural nerve on its lateral side. Afterwards it runs in the middle of the rear of the leg, pierces the deep fascia, and goes through a subfascial course between both heads of the gastrocnemius until it reaches the middle of the popliteal fossa. Here it turns inward to terminate into the popliteal vein. The posterior femoral cutaneous nerve accompanies the upper part of the vein, while going from deep to superficial.
The small saphenous vein includes 7-13 valves.
Key Points
Variations of small saphenous vein at its conclusion:
- Just before piercing the popliteal fascia, it may generate a communicating branch to the accessory saphenous vein.
- Sometimes, it stops below the knee and ends in the great saphenous vein or in the deep muscular veins of the leg.
- It may bifurcate, with 1 limb ending in the great saphenous vein and other in the popliteal vein.
Pseudo-short saphenous veins: These large muscular veins drain venous blood from 2 heads of gastrocnemius into the popliteal vein. The varicosity of these veins may mimic the varicosity of short saphenous vein; thus, they’re usually named pseudo-short saphenous veins.

 (62 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)
(62 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)