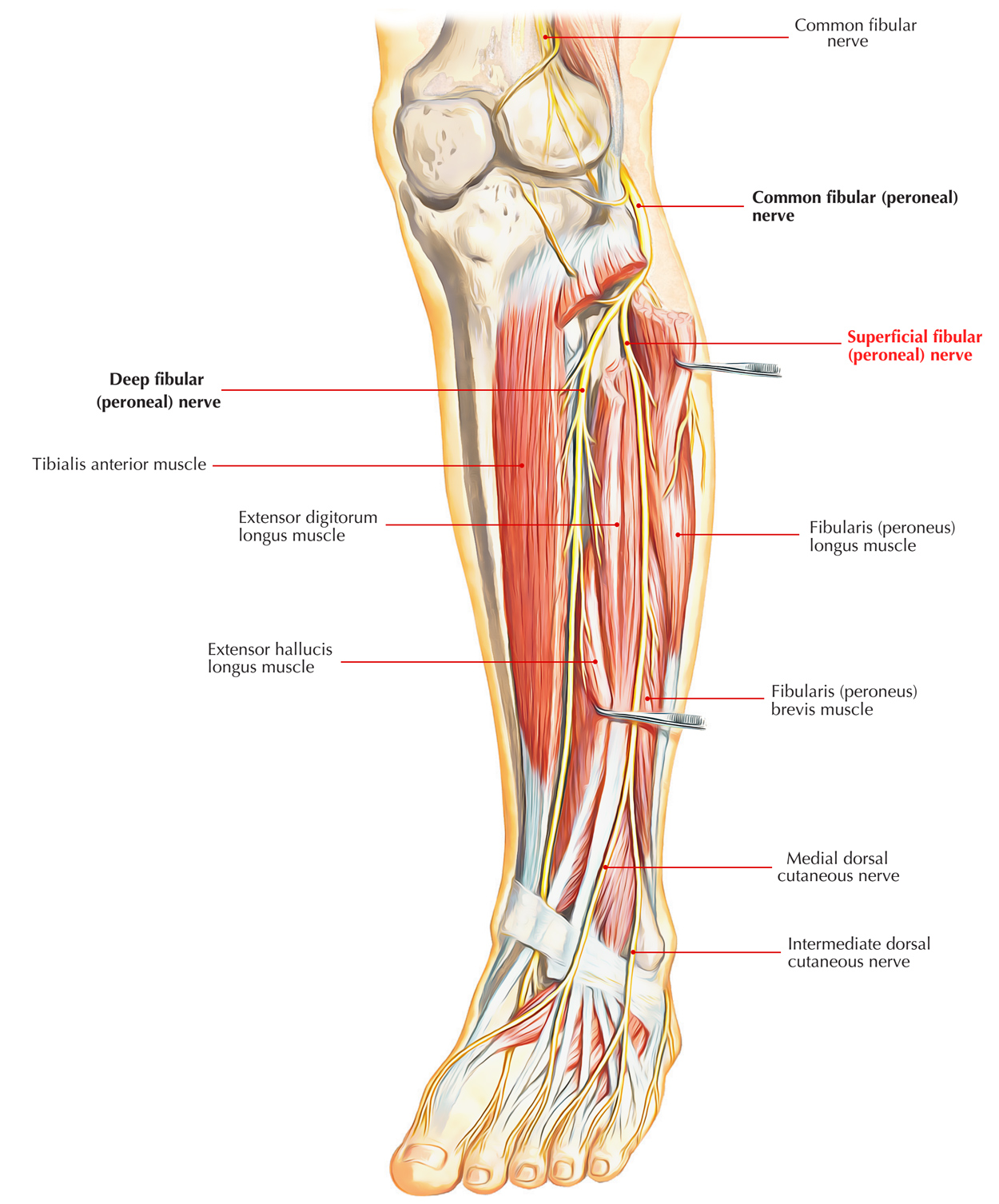
Superficial Peroneal Nerve is the nerve of the lateral compartment of the leg.
Origin
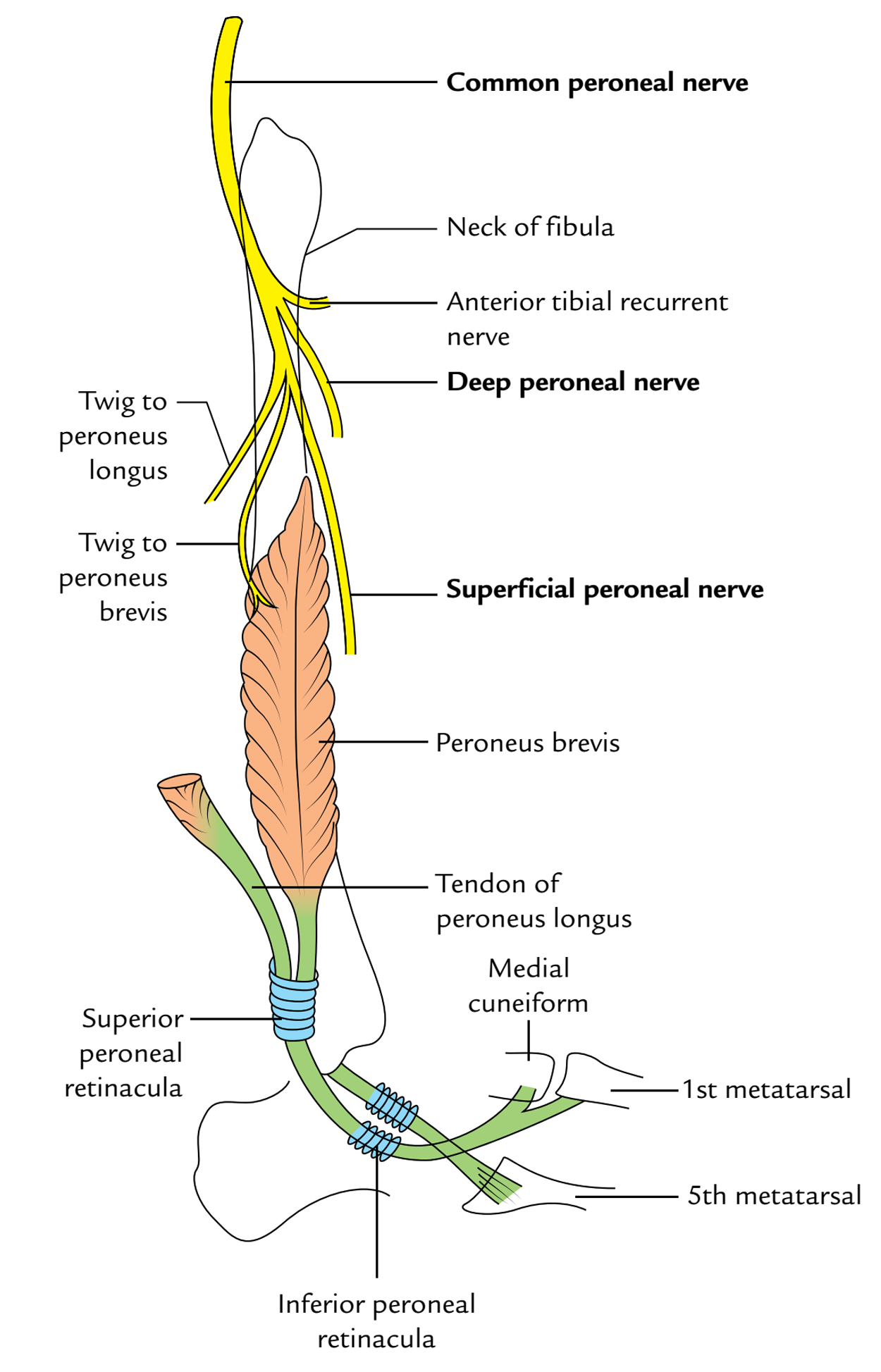
It is 1 of the 2 terminal branches of the common peroneal nerve given in the neck of the fibula. The point of origin is in the substance of peroneus longus on the lateral side of the neck of fibula.
Superficial Peroneal Nerve
Course and Relations
Its starting point is on the lateral side of the neck of the fibula and descends for a small space between the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis, and after that is located in a groove between the peroneus brevis and extensor digitorum longus.
At the junction of the upper 2/3rd and lower 1/3rd of the leg, it pierces the deep fascia, and shortly divides up into a medial and a lateral terminal branch which reaches the dorsum of the foot.
Superficial Peroneal Nerve: Course and Relation
Branches And Distribution
- Muscular branches to peroneus longus and peroneus brevis.
- Cutaneous branches provide the skin of the lower 1 third of the lateral side of the leg and dorsum of the foot, with the exception of the lands provided by the saphenous, sural, and deep peroneal nerves.
The medial terminal branch of the superficial peroneal nerve crosses the ankle and breaks up into 2 dorsal digital nerves, 1 for the medial side of the big toe and the other for the 2nd interdigital cleft.
The Lateral terminal branch of the superficial peroneal nerve also breaks up into 2 dorsal digital nerves for the third and fourth interdigital clefts.
The distribution of the superficial peroneal nerve corresponds to the distribution of radial nerve in the forearm.
Clinical Significance
Injury of superficial peroneal nerve: The injury of superficial peroneal nerve leads to:
- Loss of eversion of the foot because of paralysis of peroneus longus and peroneus brevis muscles (evertors of the foot).
- Sensory loss on the lateral aspect of the leg.
- Sensory loss on the dorsum of the foot with the exception of the web space between the first and 2nd toe and dorsal aspect of all the toes that is provided by deep peroneal nerve.

 (48 votes, average: 4.63 out of 5)
(48 votes, average: 4.63 out of 5)