Digastric Triangle also known as Submandibular Triangle is named due to it is position in the middle of the two bellies of the digastric muscle and inferior towards the base of the mandible.
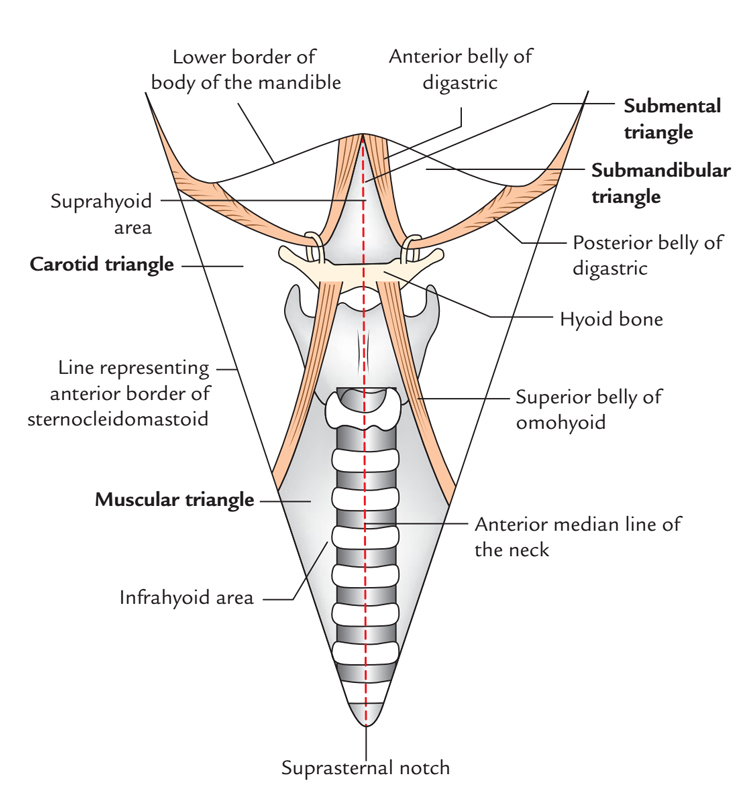
Digastric or Submandibular Triangle
Boundaries
- Anteroinferiorly: Anterior belly of digastric muscle.
- Posteroinferiorly: Posterior belly of digastric muscle, along with stylohyoid muscle.
- Base is created by the base of the mandible as well as imaginary line connecting the angle of the mandible and the mastoid process.
- Apex is created via the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle and it is connected to hyoid bone via a fascial sling arising via investing layer of deep cervical fascia.
Floor
It is formed by
- Anteriorly: Mylohyoid
- Posteriorly: Hyoglossus and small portion of the middle constrictor.
Roof
Roof is created through investing layer of deep cervical fascia, which divides in order to encompass the submandibular salivary gland. Platysma, cervical division of facial nerve and ascending branch of transverse cervical nerve are located in the superficial fascia above the roof.
Contents
The stylomandibular ligament subdivides the digastric triangle within anterior and posterior parts. The posterior portion of the triangle is superiorly constant with the parotid region.
Contents in the anterior portion of the triangle:
- Submandibular salivary gland
- Submandibular lymph nodes
- Hypoglossal nerve
- Facial vein
- Facial artery
- Submental artery
- Mylohyoid nerve and vessels
Contents in the posterior part of the triangle:
- External carotid artery
- Carotid sheath and its contents
- Structures traveling amongst the external as well as internal carotid arteries.
Divisions
The stylomandibular ligament divides into anterior and posterior parts.
Anterior Part
Anterior part consists of the submandibular gland
- Superior to gland are:
- Anterior facial vein
- Facial artery
- Glandular branches
- Beneath the gland, on the surface of the mylohyoideus are:
- Submental artery
- Mylohyoid artery
- Mylohyoid nerve
Posterior Part
Posterior portion of this triangle consists of the external carotid artery, which rises deeply inside the matter of the parotid gland.
External carotid, being crossed by the facial nerve, and gives off in its course:
- Posterior auricular
- superficial temporal
- Internal maxillary branches
More deeply are:
- Internal carotid
- Internal jugular vein
- Vagus nerve
Separated from the external carotid by:
- Styloglossus
- Stylopharyngeus
- Hypoglossal Nerve
Clinical Significance
Inflammation
Swelling is submandibular triangle because of the association of submandibular lymph nodes while they drain lymph via extensive areas like anterior two-third of tongue, with the exception of tip, floor of mouth, frontal, ethmoidal, as well as maxillary air sinuses.
Or it may be caused due to enlargement of the submandibular gland when the efferents via submandibular lymph nodes mostly pass towards jugulo-omohyoid and partially towards jugulodigastric nodes found along the internal jugular vein.

 (50 votes, average: 4.64 out of 5)
(50 votes, average: 4.64 out of 5)